When something breaks down in your car, finding the right replacement part is crucial for a smooth and cost-effective repair. Identifying the correct car part number is the first step in ensuring you get the perfect fit and the quality you expect. Whether you’re a seasoned DIY mechanic or a car owner tackling a minor repair, understanding how to locate your car part number is an invaluable skill. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about finding your car part number, ensuring you get the right part, whether you opt for Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) or aftermarket options.
Understanding OEM, Genuine, and Aftermarket Parts
Before diving into how to find your car part number, it’s important to understand the different types of car parts available: OEM, Genuine, and Aftermarket. Knowing the distinctions will help you make informed decisions when purchasing replacement components.
What are OEM Car Parts?
OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer. These parts are produced either by the original car manufacturer or by a third-party company to the exact specifications and standards set by the car manufacturer. Choosing OEM car parts means you’re getting components designed to match the quality and performance of the original parts that came with your vehicle.
OEM parts offer several benefits:
- Guaranteed Quality: They meet the stringent standards of the original car manufacturer.
- Perfect Fit: Designed specifically for your car model, ensuring seamless installation and function.
- Warranty Coverage: Often covered under your car’s warranty, providing peace of mind.
While OEM parts may sometimes be manufactured by external companies, they are made to the car manufacturer’s precise requirements. Although they might not always feature the car manufacturer’s logo, they are virtually indistinguishable from the original parts in terms of quality and specifications. In some cases, OEM parts might even be improvements over the original components.
OEM vs. Genuine Parts
The terms OEM and Genuine parts are often used interchangeably, but there’s a subtle difference. Genuine parts are manufactured directly by the car manufacturer and always carry the car manufacturer’s logo. These are the exact parts that were installed in your car when it was first assembled. In essence, all genuine parts are OEM, but not all OEM parts are genuine. OEM parts can be made by a different company that supplies the car manufacturer.
What are Aftermarket Car Parts?
Aftermarket car parts are produced by third-party companies that are not affiliated with the original car manufacturer. These parts are designed to be compatible with various makes and models of vehicles. Aftermarket parts are also known as “non-OEM” or “generic” parts.
The primary appeal of aftermarket parts is often their lower price compared to OEM parts. However, it’s crucial to consider the potential trade-offs:
- Cost Savings: Generally more affordable than OEM parts.
- Variety and Availability: A wide range of brands and options to choose from.
- Potentially Enhanced Features: Some aftermarket parts may offer improved performance or features compared to OEM equivalents.
However, there are also potential downsides:
- Variable Quality: Quality can vary significantly between different aftermarket brands.
- Fitment Issues: May not always guarantee a perfect fit compared to OEM parts designed specifically for your vehicle.
- Warranty Concerns: Using aftermarket parts might affect your car’s warranty in some cases, although this is less common for standard replacement parts.
When considering aftermarket parts, it’s important to research reputable brands and read reviews to ensure you’re choosing a quality component that meets your needs.
Methods to Find Your Car Part Number
Locating the correct part number is essential whether you’re opting for OEM or a trusted aftermarket alternative. Here are the most effective methods to find your car part number:
1. Check the Part Itself
Your first and often easiest step is to examine the part that needs replacing. Most car parts, especially OEM components, have the part number directly printed or engraved on them.
- Location: Look for a sticker, plate, or stamped marking on the part itself. Common locations include the side, back, or even underneath the component.
- Format: OEM part numbers are typically alphanumeric codes. While there isn’t a universal format, they often include a combination of letters and numbers and may contain dashes.
Unfortunately, there’s no standardized format for OEM part numbers across all manufacturers. Each car brand has its own system. For example:
- Volvo: Part numbers are generally all numeric, without dashes.
- Example: Volvo Rotor Screw (2016 – 2021):
30640811
- Example: Volvo Rotor Screw (2016 – 2021):
- Mazda: Part numbers often include letters and numbers, separated by dashes.
- Example: Mazda Reservoir Cap (2013 – 2020):
KD33-43-55 YD
- Example: Mazda Reservoir Cap (2013 – 2020):
Alt text: Close up of a Mazda Reservoir Cap showing the part number KD33-43-55 YD clearly printed on the component.
Even if you don’t immediately recognize the format, knowing where to look on the part is the first step. Clean the part if necessary to make sure the number is legible.
2. Contact the Manufacturer or Dealership
If the part number on the component is illegible due to damage or wear, or if you no longer have the old part, contacting the car manufacturer or a dealership is a reliable alternative.
- Dealership Parts Department: Contact the parts department of your local car dealership. They have access to parts catalogs and databases specific to your car’s make and model.
- Manufacturer’s Website or Customer Service: Some manufacturers offer online parts look-up tools on their websites. You can also contact their customer service directly for assistance.
When contacting a dealership or manufacturer, be prepared to provide them with detailed information about your vehicle, including:
- Make and Model: e.g., Toyota Camry, Ford F-150
- Year of Manufacture: e.g., 2018
- VIN (Vehicle Identification Number): This is the most crucial piece of information for accurate part identification.
3. Use Your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number)
Your car’s VIN, or Vehicle Identification Number, is a unique 17-digit alphanumeric code that serves as your car’s fingerprint. It contains a wealth of information specific to your vehicle, including the make, model, year, manufacturing plant, and specific features. The VIN is an incredibly powerful tool for finding the exact parts designed for your car.
- Location of VIN:
- Dashboard: The most common location is on the dashboard, visible through the windshield on the driver’s side.
- V5C Logbook (Vehicle Registration Certificate): Your car’s registration document will always list the VIN.
- Driver’s Side Doorjamb: Often found on a sticker on the driver’s side doorjamb.
- Insurance Card: Your VIN may also be printed on your car insurance card.
Alt text: Image showing the location of the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) on the dashboard of a car, visible from outside through the windshield.
- Using VIN to Find Parts:
- Online Parts Websites: Most online auto parts retailers allow you to search for parts by VIN. Simply enter your VIN into their search tool, and the system will filter parts compatible with your specific vehicle.
- Dealerships and Parts Stores: When you visit a dealership or auto parts store, providing your VIN allows the parts specialists to quickly and accurately identify the correct parts for your car.
The VIN ensures you get parts that are guaranteed to fit your exact vehicle configuration, accounting for variations within the same make and model year.
Youngcardriver.com provides a helpful diagram breaking down the meaning of each section of the VIN:
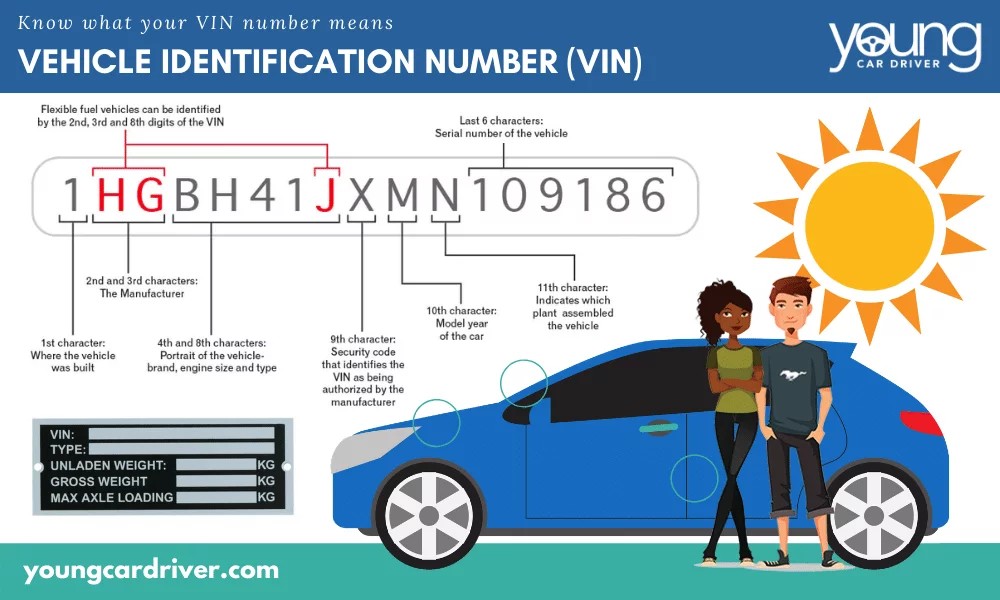 VIN explanation digram
VIN explanation digram
If you can’t find the VIN on your dashboard, check these additional locations on your car:
- Driver’s side front door frame column
- Machined pad on the front of the engine
- Inside the left side wheel arch
- Steering wheel or steering column
- Radiator support bracket
Once you have your VIN, you can confidently use it to find the precise OEM or compatible aftermarket part you need.
OEM vs. Aftermarket Parts: Making the Right Choice
After successfully finding your car part number and identifying potential replacement options, the next decision is whether to choose OEM or aftermarket parts. Both options have their advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice depends on your specific needs and priorities.
Here’s a comparison to help you decide:
| Feature | OEM Parts | Aftermarket Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Generally more expensive | Typically less expensive |
| Quality | Guaranteed to meet original manufacturer standards | Quality can vary; reputable brands offer good quality |
| Fitment | Perfect fit guaranteed for your vehicle model | Fit can sometimes be less precise; check compatibility |
| Warranty | Often covered by car warranty | Warranty varies by brand and part |
| Availability | Readily available through dealerships | Widely available from various retailers |
| Branding | May have car manufacturer or OEM brand | Branded by the third-party manufacturer |
| Performance | Designed to match original performance | Performance can be equal to, better, or worse than OEM |
Pros of OEM Parts:
- Reliability: Known for their durability and performance, matching the original part.
- Peace of Mind: Guaranteed fit and often backed by warranty.
Cons of OEM Parts:
- Higher Cost: Can be significantly more expensive than aftermarket options.
Pros of Aftermarket Parts:
- Affordability: Offers budget-friendly alternatives.
- Variety: Wide selection of brands and price points.
- Potential Upgrades: Some aftermarket parts are designed to improve performance or durability over OEM.
Cons of Aftermarket Parts:
- Quality Variability: Quality differs greatly between brands; research is essential.
- Fitment Concerns: While many are designed to fit, perfect fit isn’t always guaranteed.
Making Your Decision:
- Budget: If cost is a major concern, aftermarket parts can be a viable option, but prioritize reputable brands.
- Quality and Longevity: For critical components, OEM parts offer assured quality and longevity.
- Vehicle Value: For newer or higher-value vehicles, maintaining OEM quality might be preferable to preserve resale value and performance.
- Complexity of Repair: For simple, non-critical parts, well-reviewed aftermarket options can be cost-effective. For complex or safety-related repairs, OEM might be the safer choice.
Conclusion
Finding the right car part number is the foundation for successful car repairs and maintenance. By using methods like checking the part itself, contacting the manufacturer, or leveraging your VIN, you can confidently identify the component you need. Understanding the differences between OEM, genuine, and aftermarket parts empowers you to make informed decisions based on your budget, quality expectations, and vehicle needs. Whether you choose the guaranteed quality of OEM or the value of aftermarket, knowing how to find your car part number ensures you’re on the right track to getting your vehicle back in top shape.