Following the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), the focus of treatment transitions from the immediate cardiac arrest algorithm to a more systematic approach. This phase, known as post-cardiac arrest care, is critical for stabilizing the patient and improving outcomes. It emphasizes a structured method of evaluation, identification, and intervention to address organ system dysfunction that commonly occurs after cardiac arrest.
The primary objective of post-cardiac arrest care is to reduce morbidity and mortality by meticulously assessing and managing the respiratory, cardiovascular, and neurologic systems. Optimizing oxygenation, ventilation, and perfusion are paramount goals during this phase. These measures are essential to stabilize cardiopulmonary function and, crucially, to preserve neurologic function, which is often compromised during and after cardiac arrest.
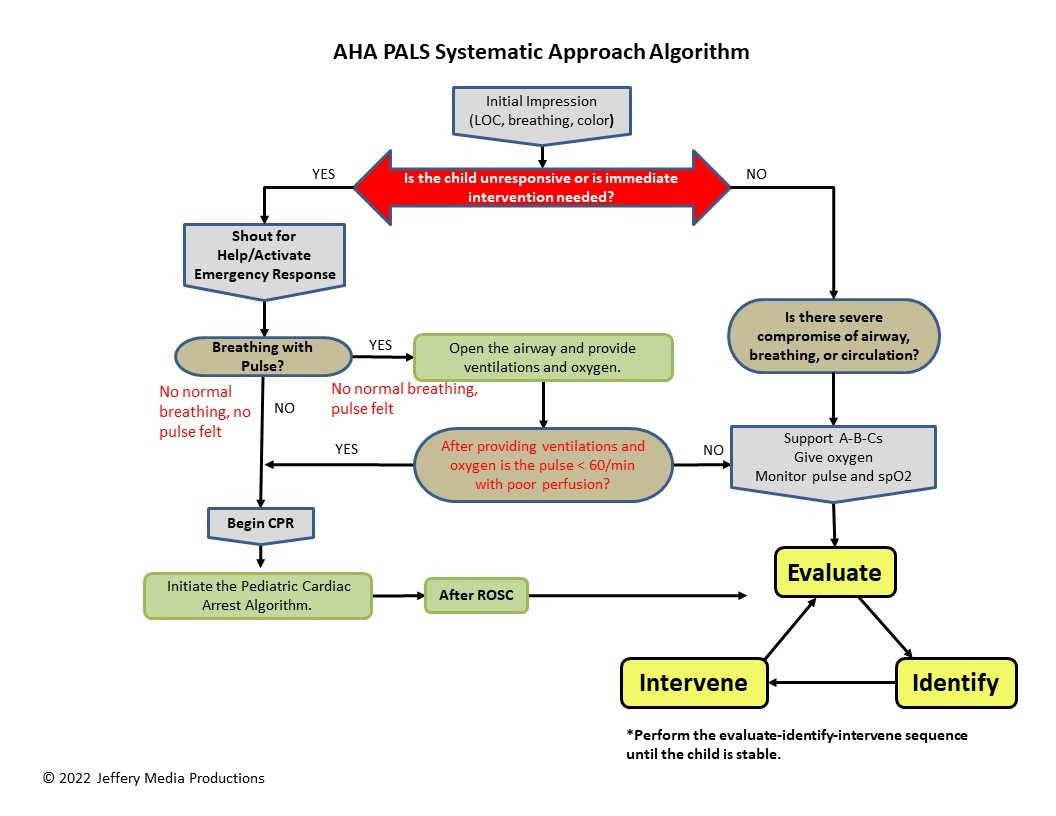 pals-systematic-approach-algorithm
pals-systematic-approach-algorithm
Systematic Approach to Post Cardiac Arrest Care
Post-cardiac arrest care employs a systematic approach that prioritizes the stabilization of vital organ systems. This involves setting specific goals, implementing targeted interventions, and conducting thorough assessments for each system.
Respiratory System Care
Goals: The main goals for respiratory system care are to optimize and stabilize the patient’s airway, ensure adequate oxygenation, and support effective ventilation.
Interventions: Initial interventions include confirming the correct placement of the endotracheal (ET) tube if intubation was performed. Providing adequate oxygenation and ventilation is crucial, often requiring mechanical ventilation to support breathing and maintain appropriate oxygen saturation levels.
Assessments: Continuous monitoring is essential. This includes capnography to monitor end-tidal carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, arterial blood gas analysis to evaluate oxygenation and ventilation status, and chest X-rays to verify ET tube placement and assess for any lung pathology.
Cardiovascular System Care
Goals: The goals for the cardiovascular system are to support tissue perfusion, maintain cardiovascular function, and prevent the onset of shock, a common complication following cardiac arrest.
Interventions: Interventions focus on maintaining adequate blood pressure and perfusion to vital organs. This may involve the use of intravenous fluids and vasopressors to support blood pressure. Treating arrhythmias is also a key intervention, as abnormal heart rhythms can further compromise cardiovascular stability.
Assessments: Assessing tissue perfusion is vital. This is achieved by monitoring lactate concentration, venous oxygen saturation, and base deficit, which are indicators of tissue oxygen delivery. Hemodynamic monitoring, including intra-arterial blood pressure measurement, provides continuous blood pressure readings. Urine output, capillary refill time, and skin temperature are also monitored as clinical indicators of perfusion.
Neurologic System Care
Goals: The primary goal for neurologic system care in the post-cardiac arrest phase is neurologically intact survival. Protecting the brain from further injury and promoting recovery are paramount.
Interventions: Targeted temperature management (TTM) is a critical intervention to improve neurologic outcomes. Avoiding hyperthermia (elevated body temperature) is equally important. Adequate analgesia and sedation are provided to manage pain and agitation, and to reduce metabolic demand. Seizures and increased intracranial pressure are treated promptly if they occur. Hyperventilation is avoided as it can be detrimental to cerebral blood flow.
Assessments: Continuous monitoring of core body temperature is necessary for effective TTM. Point-of-care blood glucose levels are monitored to prevent hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, which can affect neurologic function. Ongoing neurological assessments are performed to detect changes in neurologic status and guide further interventions.
In conclusion, post-cardiac arrest care is a multifaceted and critical phase following ROSC. It encompasses a systematic approach to managing the respiratory, cardiovascular, and neurologic systems. Effective post-cardiac arrest care, focused on these key areas, significantly improves the chances of patient survival with good neurological outcomes.

