Have you ever struggled to describe a car part when discussing repairs or accidents? It’s a common issue! At [cardiagxpert.com], we believe that clear communication is key, especially when it comes to auto repairs. Understanding the basic Names Of Car Body Parts empowers you to accurately explain issues and understand repair estimates. Forget using vague terms like “thingy” or “whatchamacallit” – let’s get familiar with the proper terminology.
This guide will provide you with a simple overview of common car body part names. We’ll use clear and straightforward terms, focusing on driver and passenger sides for easy understanding, regardless of your perspective facing the vehicle.
Let’s dive into the anatomy of your car!
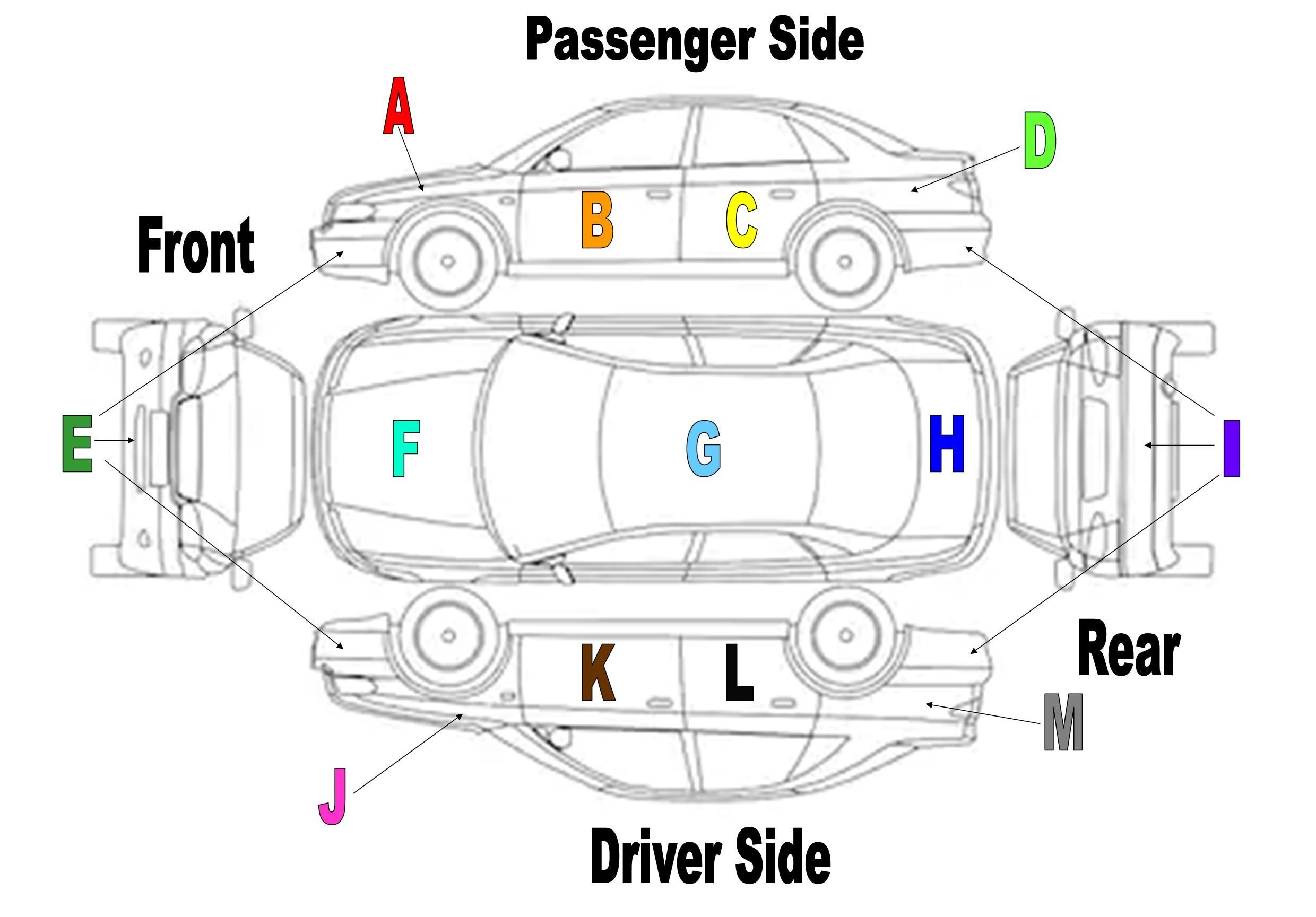 Diagram of common car body parts with labels
Diagram of common car body parts with labels
Key Car Body Panel Names You Should Know
Here’s a breakdown of the common names for car body panels, referencing the diagram above for visual clarity:
- A – Passenger Side Fender: The fender is the panel that frames the front wheel well. It protects the car’s body and pedestrians from debris thrown up by the tire.
- B – Passenger Side Door: The door provides access to the vehicle’s cabin. Modern cars have complex door structures including windows, locking mechanisms, and side impact beams.
- C – Rear Passenger Side Door: Similar to the front door, but positioned for rear passenger access. On some models, the rear door design and size may differ significantly from the front.
- D – Passenger Side Quarter Panel: This panel is located between the rear door and the rear bumper. The quarter panel is a significant structural part of the car’s body, often extending to the roof.
- E – Front Bumper: The front bumper is designed to absorb impact in a low-speed collision, protecting the car’s body and safety systems. Bumpers are often made of plastic or reinforced materials.
- F – Hood: Also known as the bonnet, the hood covers the engine compartment. It provides access for maintenance and repairs and also plays a role in aerodynamics.
- G – Roof: The roof forms the upper covering of the car, providing structural integrity and protection from the elements. Roof designs vary greatly across car models, including sunroofs or panoramic roofs.
- H – Trunk: Referred to as the boot in some countries, the trunk is the main storage compartment at the rear of the vehicle. Trunk designs and sizes vary greatly depending on the car type.
- I – Rear Bumper: Similar to the front bumper, the rear bumper protects the vehicle from rear-end collisions. It often houses sensors for parking assist and other safety features.
- J – Driver Side Fender: Mirrors the passenger side fender, framing the driver’s side front wheel well and offering similar protection.
- K – Driver Side Door: The main access point for the driver, often equipped with controls for windows, mirrors, and door locks.
- L – Rear Driver Side Door: Provides access to the rear passenger area on the driver’s side. Its design is usually consistent with the rear passenger side door.
- M – Driver Side Quarter Panel: The rear panel on the driver’s side, mirroring the passenger side quarter panel and contributing to the car’s structural integrity.
Understanding these basic car body part names can significantly improve communication with auto repair professionals. It helps ensure everyone is on the same page, leading to more accurate diagnoses and efficient repair processes. Knowing the difference between a fender and a quarter panel, for instance, can prevent misunderstandings and ensure you receive the correct repair service.
While this is a basic overview, familiarity with these terms is a great starting point. For more detailed information on specific auto body repair services, explore the resources available on [cardiagxpert.com]. Being informed about your car empowers you to make better decisions about its care and maintenance.