Understanding the different parts of a car is essential knowledge for vehicle owners, mechanics, and anyone interested in the automotive world. Whether you’re performing maintenance, discussing repairs, or simply expanding your vocabulary, knowing the names of car body parts is incredibly useful. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of car body parts with pictures, making identification straightforward and enhancing your understanding of automotive anatomy.
Essential Car Body Parts Names
Before we delve into specific sections, let’s clarify the terminology for “car” itself. In English, “car” is the standard term. You might also hear “automobile” or “vehicle,” but “car” is the most common and universally understood.
Interior Car Body Parts
The interior of a car is where drivers and passengers interact most directly with the vehicle. Familiarity with these car body parts is essential for comfortable and safe driving.
| Part Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Accelerator Pedal | Controls the car’s speed by regulating fuel flow to the engine. |
| Brake Pedal | Used to slow down or stop the vehicle by applying pressure to the braking system. |
| Clutch Pedal | (Manual transmissions only) Disengages the engine from the transmission to allow gear changes. |
| Gear Shift | Selects different gears to control the car’s speed and power output. |
| Glove Compartment | A storage space built into the dashboard, often used for documents and small items. |
| Handbrake (Parking Brake) | Mechanically engages the brakes to keep the vehicle stationary, especially when parked. |
| Horn | A sound-signaling device used to alert others, typically in emergency situations. |
| Floor Mats | Protective coverings for the car’s floor, trapping dirt and debris. |
| Rearview Mirror | Provides a view of the area behind the vehicle, essential for safe reversing and lane changes. |
| Seatbelt | A safety harness designed to restrain occupants in the event of a collision, significantly reducing injury risk. |
| Seats | Provide seating for the driver and passengers, designed for comfort and support. |
| Steering Wheel | Controls the direction of the vehicle by turning the front wheels. |
| Power Steering | System that assists steering, making it easier to turn the steering wheel, especially at low speeds. |


Exterior Car Body Parts
The exterior car body parts are what define a car’s shape and protect its internal components from the elements and impacts. Understanding these terms is crucial for describing a car’s appearance and discussing potential damage.
| Part Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Bumper | Front and rear protective bars designed to absorb impact in low-speed collisions, minimizing damage to the car’s structure. |
| Door Handles | Mechanisms used to open and close the car doors. |
| Doors | Hinged panels that provide access to the car’s interior. |
| Fenders (Front and Rear) | Body panels that surround the wheel wells, protecting the car from road debris and reducing spray. |
| Grill | Located at the front of the car, it allows air to flow to the radiator and engine while often serving as a design feature. |
| Headlights | Powerful front lights that illuminate the road ahead for nighttime driving and improve visibility in poor conditions. |
| Hood (Bonnet) | Hinged cover over the engine compartment, providing access for maintenance and repairs. |
| Hubcaps (Wheel Covers) | Decorative covers for the center of the wheels, enhancing appearance and protecting wheel bearings. |
| Indicator Lights (Turn Signals) | Flashing lights at the front and rear of the car, signaling intended turns or lane changes. |
| License Plate | A registration plate attached to the front and rear of the vehicle, legally identifying it. |
| Side Mirrors (Outside Mirrors) | Provide visibility of the sides of the vehicle and eliminate blind spots for safe lane changes and turns. |
| Roof | The top panel of the car, providing structural integrity and protection from weather. |
| Sunroof (Moonroof) | An opening in the car roof that can be opened to allow light and fresh air into the cabin. |
| Tail Light | Rear lights that indicate the car’s presence, especially at night, and signal braking or turning. |
| Trunk (Boot) | Rear storage compartment for luggage and cargo. |
| Wheels | Circular components that allow the car to move by rotating around an axle, typically fitted with tires. |
| Windows | Transparent panels in the doors and body, providing visibility and protection from the elements. |
| Windshield (Windscreen) | The front window of the car, designed to provide a clear view of the road ahead and protect occupants from wind and debris. |
| Windshield Wipers | Mechanical arms with rubber blades that clear rain, snow, and debris from the windshield to maintain visibility. |
Under the Hood Car Body Parts (Mechanical Components)
The parts under the hood are the mechanical heart of the car. While technically not all “body parts,” understanding these components is vital for car maintenance and repair knowledge.
| Part Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Air Filter | Cleans the air entering the engine, preventing dust and debris from causing damage. |
| Alternator | Generates electrical power to charge the battery and run electrical systems while the engine is running. |
| Battery | Stores electrical energy to start the engine and power electrical components when the engine is off. |
| Belt (Serpentine Belt) | A long, winding belt that drives multiple engine accessories like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. |
| Camshaft | Controls the opening and closing of engine valves in precise synchronization with the pistons. |
| Carburetor | (Older vehicles) Mixes air and fuel for combustion in the engine. Modern cars use fuel injection. |
| Catalytic Converter | Reduces harmful emissions from the exhaust gases, converting pollutants into less harmful substances. |
| Coil (Ignition Coil) | Part of the ignition system that generates high voltage to create a spark at the spark plugs, igniting the air-fuel mixture. |
| Combustion Chamber | The space within the cylinder where the air-fuel mixture is burned to produce power. |
| Crankshaft | Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which powers the car. |
| Fuel Pump | Pumps fuel from the fuel tank to the engine. |
| Ignition System | The system responsible for initiating the combustion process in the engine, typically involving spark plugs and coils. |
| Piston Rod (Connecting Rod) | Connects the piston to the crankshaft, transmitting force between them. |
| Pulley | A grooved wheel that helps transmit power via belts to various engine accessories. |
| Radiator | Cools the engine coolant, preventing the engine from overheating. |
| Exhaust Valve | Controls the release of exhaust gases from the combustion chamber. |
| Thermostat | Regulates engine temperature by controlling coolant flow to the radiator. |
| Vacuum Diaphragm | Used in various engine control systems, often in older vehicles, to regulate vacuum pressure. |
| Valve (Engine Valve) | Controls the flow of intake air and exhaust gases into and out of the engine cylinders. |
| Voltage Regulator | Maintains a constant voltage level in the car’s electrical system, protecting components from voltage spikes. |
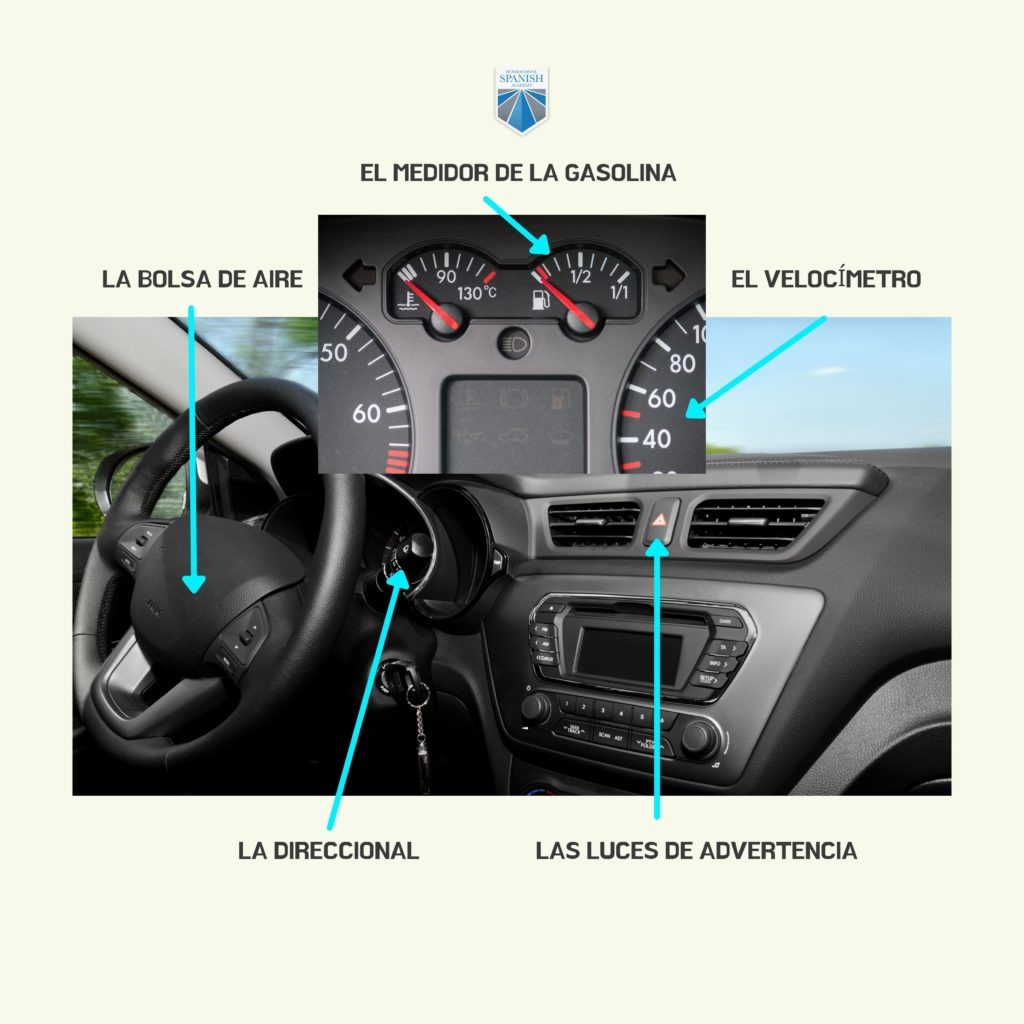
Instrument Panel Car Body Parts
The instrument panel, or dashboard, houses crucial gauges and indicators that provide the driver with essential information about the vehicle’s operation.
| Part Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Airbag Indicator | Warning light that indicates a problem with the airbag system. |
| Fuel Gauge | Displays the amount of fuel remaining in the fuel tank. |
| Speedometer | Indicates the vehicle’s current speed. |
| Turn Signal Indicator | Lights on the dashboard that flash to confirm the operation of the turn signals. |
| Warning Lights | Various lights that illuminate to indicate potential problems or malfunctions, such as low oil pressure or engine temperature. |
Conclusion
Understanding car body parts is more than just automotive jargon; it’s practical knowledge that empowers you to communicate effectively about your vehicle, whether with mechanics, parts suppliers, or fellow car enthusiasts. Using this guide with Car Body Parts Pictures, you can now confidently identify and name the key components of a car, enhancing your automotive literacy and preparedness for car ownership and maintenance.
To further expand your automotive knowledge, consider exploring resources on basic car maintenance and repair. Learning to identify these parts visually and by name is the first step towards deeper understanding and confident interaction with the world of automobiles.