Have you ever wondered about the different parts that make up your car’s exterior? Just like the human body has various parts that work together, a car is composed of numerous body parts, each with its specific function. Understanding these components is crucial for car maintenance, repair, and even just general knowledge.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the major car body parts, providing you with a detailed list, a helpful diagram, and clear explanations of each part’s role. Whether you’re a car enthusiast, a student learning about automotive technology, or simply a car owner wanting to be more informed, this article will enhance your understanding of your vehicle’s anatomy.
Car Body Parts Diagram
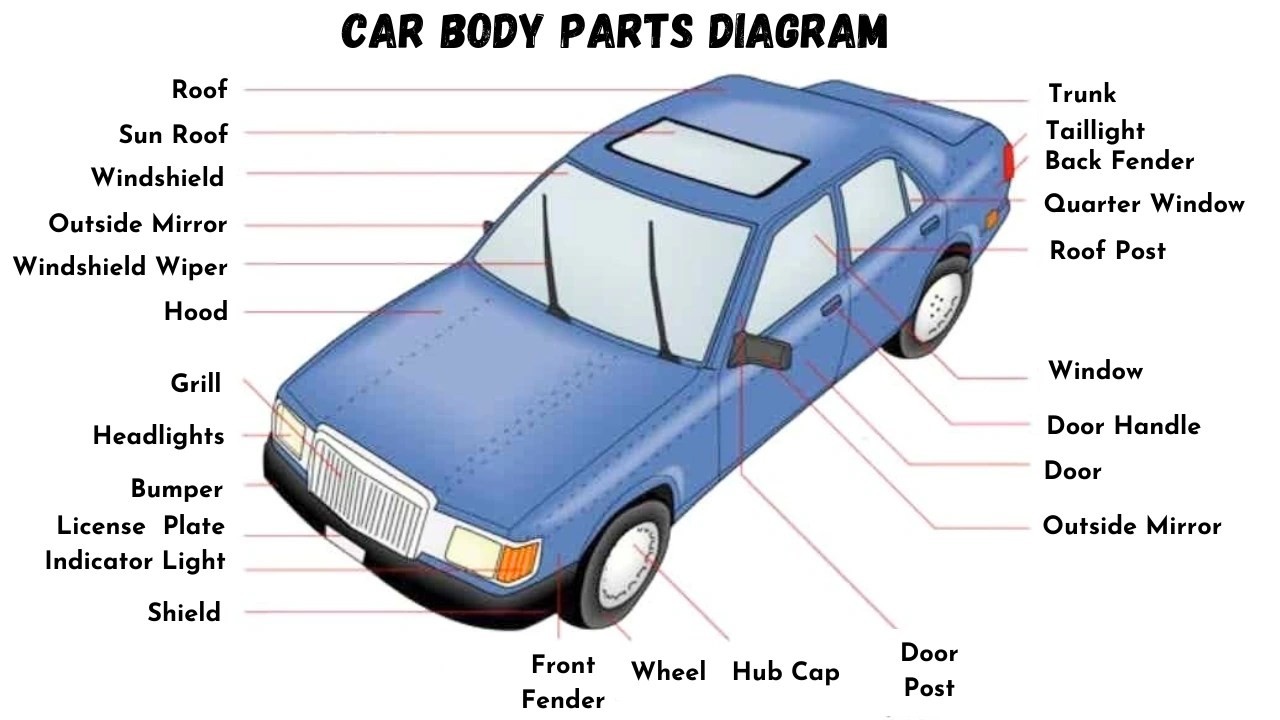 Car Body Parts Diagram
Car Body Parts Diagram
Alt text: Detailed car body parts diagram with names, illustrating exterior components like hood, bumper, fender, roof, door, wheel, and lights.
Detailed Car Body Parts List with Names and Functions
The car body is composed of a variety of parts, each designed for specific functions, from protection and aerodynamics to aesthetics. Below is a detailed list of the most common car body parts, along with a description of their purpose.
#1. Body Shell
The body shell is the foundational structure of your car. Think of it as the skeleton. It’s the main structural component upon which all other parts are attached, including the engine, chassis, and interior. The body shell provides rigidity and shape to the car, contributing to its overall safety and structural integrity. It’s the underlying framework before doors, windows, and other external and internal fittings are added.
#2. Hood or Bonnet
The hood, also known as the bonnet in some regions, is the hinged cover at the front of the car that protects the engine compartment. Its primary function is to shield the engine and related components from the elements, such as rain, snow, and debris. Furthermore, it provides convenient access to the engine bay for routine maintenance, fluid checks, and repairs. Hoods are typically made of steel or aluminum, but aftermarket options can include lighter materials like carbon fiber for performance vehicles.
#3. Front Bumper
The front bumper is a crucial safety component mounted at the front of the vehicle. It is designed to absorb impact during low-speed collisions, minimizing damage to the car’s body and internal structures. Modern front bumpers are often constructed from energy-absorbing plastics and may incorporate features like grilles and fog lights. They extend around the front corners of the car, partially covering the wheel arches for added protection.
#4. Rear Bumper
Similar to the front bumper, the rear bumper provides protection to the vehicle’s rear end. It is designed to absorb impact in rear-end collisions, safeguarding the trunk, taillights, and exhaust system from costly damage. Rear bumpers often house or integrate with taillights, parking sensors, and the license plate. Both front and rear bumpers are essential for vehicle safety and reducing repair costs from minor accidents.
#5. Bumper Grille
The bumper grille is an opening in the bumper, typically made of mesh or slats, that allows air to flow into the engine compartment. Located between the headlights, the grille’s primary function is to provide ventilation for the engine and radiator, aiding in cooling and preventing overheating. Grille designs vary greatly between car manufacturers and models, contributing to the vehicle’s distinctive front-end styling.
#6. Crash Guard or Bullbar
Crash guards, also known as bullbars, are robust metal bars installed on the front (and sometimes rear) of a vehicle for added protection. Primarily used on SUVs and trucks, they are designed to protect the vehicle from damage in collisions, especially in off-road conditions or impacts with animals. While offering enhanced protection, bullbars can sometimes affect pedestrian safety and vehicle aerodynamics.
#7. Headlight
Headlights are essential lighting components mounted at the front of the car, providing illumination for the road ahead during nighttime or low-visibility conditions. Modern headlights utilize various technologies, including halogen, LED, and xenon, to provide bright and focused beams. They are crucial for safe driving, enabling the driver to see obstacles and be seen by other road users.
#8. Fog Lamp
Fog lamps are specialized lights designed to improve visibility in dense fog, heavy rain, or snow. Mounted lower than headlights, fog lamps produce a wide, low beam that cuts through fog and illuminates the road surface directly in front of the vehicle. They are a valuable safety feature for driving in adverse weather conditions, complementing the function of headlights.
#9. Indicator Lights
Indicator lights, also known as turn signals or blinkers, are flashing lights located at the front, sides, and rear of the vehicle. Their primary function is to signal the driver’s intention to turn or change lanes to other road users. They are a critical communication tool for safe navigation and maneuvering on roads, ensuring predictability and preventing accidents.
#10. Wiper Blade
Wiper blades are essential components of the windshield wiper system, responsible for cleaning the windshield and maintaining clear visibility in rain, snow, or when the windshield is dirty. Made of rubber, wiper blades sweep across the windshield, removing water, debris, and grime. Regular replacement of wiper blades is important for optimal visibility and driving safety.
#11. Radiator
The radiator is a key component of the engine cooling system. It’s a heat exchanger that dissipates heat from the engine coolant, preventing the engine from overheating. Located behind the front grille, the radiator receives airflow while the car is moving, facilitating the cooling process. Maintaining a properly functioning radiator is crucial for engine longevity and performance.
#12. Radiator Supports
Radiator supports are structural elements that hold the radiator in place within the engine bay. They provide a stable mounting point for the radiator and ensure it is properly positioned to receive airflow for cooling. These supports are typically made of metal and are designed to withstand vibrations and stresses from driving conditions.
#13. Cowl Panel
The cowl panel is the area at the base of the windshield, often housing the windshield wipers and vents for the car’s ventilation system. It’s located between the hood and the windshield and serves as a transition area between the engine compartment and the passenger cabin. The cowl panel also helps to channel water away from the cabin and into the drainage system.
#14. Quarter Panel
The quarter panel is a body panel located between the rear door and the trunk (or taillights) and extends to the rear wheel arch. It’s a significant structural part of the car’s side and rear, often encompassing the rear wheel well. Damage to the quarter panel can be more complex to repair due to its structural role and integration with other body components.
#15. Fender
Fenders, sometimes called wings, are body panels that frame the wheel arches. They are designed to protect the car’s body and occupants from debris, mud, and water thrown up by the tires. Fenders also contribute to the car’s aerodynamics and styling. Front fenders are located in front of the front doors, while rear fenders are positioned behind the rear doors or as part of the quarter panel.
Alt text: Close-up of a car fender, showing its curved shape and protective function over the wheel.
#16. Fender Liners
Fender liners, also known as wheel well liners or inner fenders, are plastic or composite shields that fit inside the wheel wells, behind the fenders. They provide an additional layer of protection to the fenders and the car’s underbody from moisture, road salt, and debris. Fender liners help to prevent corrosion and extend the lifespan of these critical areas.
#17. Roof
The roof is the topmost body panel of the car, providing overhead protection for the occupants from the elements. Roofs come in various styles, including hardtops, convertibles, and sunroof models. The roof contributes significantly to the car’s structural integrity and rollover protection.
#18. Sunroof
A sunroof is a movable panel in the car roof that can be opened to allow light and fresh air into the cabin. Sunroofs can be manually operated or power-operated and are available in different sizes and designs, including sliding, pop-up, and panoramic versions. They enhance the driving experience by offering an open-air feel.
#19. Mirrors
Car mirrors are essential for driver visibility, allowing the driver to see areas around the vehicle that are not in their direct line of sight. They include rearview mirrors (inside the car) and side mirrors (mounted on the doors). Mirrors are crucial for safe lane changes, parking, and general awareness of the surrounding traffic.
#20. Doors
Car doors provide access to the vehicle’s interior for occupants. They are hinged panels that can be opened and closed, and they incorporate features like windows, door handles, and locking mechanisms. Doors also contribute to the car’s side impact safety and structural rigidity. Cars can have two-door, four-door, or even configurations like sliding doors on vans.
#21. Door Handle
Door handles are the mechanisms used to open and close car doors. They can be exterior handles, used to open the door from outside the car, and interior handles, used to open the door from inside. Door handles come in various designs, from traditional levers to modern electronic and flush-mounted types.
#22. Window Glass
Window glass is used for the car’s windows, providing visibility, protection from the elements, and insulation. Car window glass is typically tempered for safety, meaning it shatters into small, relatively harmless pieces upon impact. Windows can be fixed or operable (roll-up/down) and may have features like tinting or defogging.
#23. Quarter Window
A quarter window is a smaller window located in the quarter panel, typically behind the rear doors or in the rear pillar area. It enhances visibility and can contribute to the car’s styling. Some quarter windows are fixed, while others may be small vent windows that can be opened.
#24. Trunk or Decklid
The trunk, also known as the decklid on some cars, is the hinged cover that provides access to the vehicle’s cargo area at the rear. It secures the trunk space and protects the contents from the elements. Trunks can be opened manually or with power assistance and come in various configurations, such as traditional hinged lids or liftbacks.
#25. Mud Flaps
Mud flaps, also known as splash guards, are panels mounted behind the wheels, particularly the rear wheels. They are designed to prevent mud, water, and road debris from being thrown up by the tires and hitting the car’s body or other vehicles. Mud flaps are especially useful in wet or unpaved road conditions, protecting the paint and undercarriage from damage.
#26. Wheels
Wheels are the circular components that allow the car to move by rolling along the road surface. They consist of a rim (the outer edge) and a tire mounted onto it. Wheels are crucial for vehicle mobility and are connected to the axles and suspension system. Wheel designs vary widely in size, material, and style, affecting both performance and aesthetics.
#27. Hubcap
Hubcaps, also known as wheel covers, are decorative disks that fit over the center of the wheel. They are primarily for aesthetic purposes, concealing the lug nuts and the center of the wheel for a cleaner and more finished look. Hubcaps can be made of plastic or metal and come in various designs to complement the car’s styling.
#28. Dashboard
The dashboard, also known as the instrument panel, is the control panel located inside the car, directly in front of the driver. It houses instruments like the speedometer, tachometer, fuel gauge, and warning lights, providing essential information to the driver. The dashboard also integrates controls for various vehicle functions, such as the radio, climate control, and navigation system.
#29. Number Plate
The number plate, also known as the license plate, is a metal or plastic plate attached to the front and rear of the vehicle. It displays the vehicle’s registration number, which is unique to each car and used for identification purposes. Number plates are legally required for vehicle operation and are issued by government authorities.
#30. Taillights
Taillights are lighting assemblies mounted at the rear of the vehicle. They serve multiple functions, including indicating the vehicle’s presence to other drivers, signaling braking (brake lights), and indicating turns (integrated with indicator lights). Taillights are crucial for rear visibility and communication, enhancing safety, especially in low-light conditions or when braking.
FAQs
What are the main body parts of a car?
The main body parts of a car include the body shell, hood, bumpers (front and rear), fenders, roof, doors, and trunk. These are the primary exterior components that define the car’s shape, protect internal parts, and contribute to its structural integrity.
What are car panels called?
Car panels refer to the various sheet metal or composite sections that make up the car’s exterior body. These include the hood, fenders, doors, roof, quarter panels, and trunk lid. Each panel is shaped and designed to fit together to form the car’s overall body structure and aerodynamic profile.
What is the most important part of a car?
While every part of a car is important for its overall function, the engine and the chassis are often considered the most critical. The engine provides the power to propel the vehicle, and the chassis is the structural framework that supports all other components and ensures the car’s stability and safety. However, all systems must function correctly for safe and reliable operation.
How do I find the name of a car part?
To identify a car part, you can:
- Check your car’s owner’s manual: It often includes diagrams and lists of parts.
- Use online parts catalogs: Websites specializing in car parts often have diagrams and part finders.
- Consult a mechanic: A professional mechanic can quickly identify any car part.
- Look for part numbers: Many car parts have a part number stamped or labeled on them, which can be used to search online or at a parts store.
- Use visual search: Take a picture of the part and use image search on Google or specialized parts websites.
What is the front body of a car called in the UK?
In the UK, the front body of a car that covers the engine is called the bonnet. In American English, this part is referred to as the hood. Both terms refer to the same component.
Conclusion
Understanding the names and functions of car body parts is beneficial for every car owner. It enhances your ability to communicate with mechanics, perform basic maintenance, and better appreciate the engineering and design of your vehicle. This guide, complete with a diagram and detailed descriptions, serves as a valuable resource for expanding your automotive knowledge.