Have you ever wondered about the names of all the different parts that make up the exterior of your car? Just like understanding human anatomy, knowing the components of your vehicle’s exterior is incredibly useful for maintenance, repairs, and even just appreciating automotive design. This guide will walk you through a comprehensive Car Exterior Parts Diagram and detailed descriptions of each part, enhancing your understanding of your car’s outer structure.
Exploring the Car Body: A Detailed Breakdown
The exterior of your car isn’t just about aesthetics; each part plays a vital role in safety, aerodynamics, and overall vehicle functionality. Let’s delve into the main components you’ll find on most vehicles, providing a clear car exterior parts diagram for easy identification.
Core Car Body Structure
The foundation of your car’s exterior starts with the main structural elements, providing shape and protection.
#1. Body Shell
The body shell is the primary structural component of the car’s body. Think of it as the skeleton onto which all other exterior parts are attached. It’s the underlying framework that defines the car’s shape, excluding detachable parts like doors, and the hood. The body shell provides structural integrity, safety in collisions, and a base for mounting mechanical and electrical systems.
#2. Roof and Pillars
The roof is the uppermost part of the car, shielding occupants from the elements. It’s supported by pillars, which are vertical structural posts. Pillars are crucial for roof support and overall vehicle strength, especially in rollover situations. Cars typically have A, B, and C pillars (and sometimes D pillars in larger vehicles), each located at different points along the cabin.
#3. Doors
Doors are essential for entry and exit from the vehicle. They are more than just panels; they incorporate features like door locks, windows, hinges, and sometimes integrated speakers or storage. The number of doors varies by vehicle type, from two-door coupes to four-door sedans and beyond.
#4. Windows
Windows are transparent panels that allow visibility and light into the cabin while protecting occupants from wind and weather. The main windows include the windshield (front), side windows, and rear window. Modern cars often feature power windows that can be raised and lowered electronically.
Front Exterior Components
The front of your car is designed for aerodynamics, engine cooling, and pedestrian safety.
#5. Hood/Bonnet
The hood, also known as the bonnet in some regions, is the hinged cover over the engine compartment at the front of the vehicle. Its primary functions are to protect the engine and its components from the elements and to provide easy access for maintenance and repairs. Hoods are usually made of steel or aluminum, and often include a latch for secure closure.
#6. Front Bumper
The front bumper is a protective bar at the front of the car designed to absorb impact in low-speed collisions. It’s crucial for minimizing damage to the body shell, headlights, and grille. Bumpers are typically made of plastic or reinforced composite materials and are designed to meet specific safety standards.
#7. Grille
The grille is located at the front of the car, often between the headlights. It’s designed with openings to allow airflow to the engine radiator for cooling. Grilles come in various designs and are often a key styling element of a vehicle, contributing to brand identity. Different types include main grilles, lower grilles, and fog light grilles.
#8. Headlights
Headlights are essential lighting components mounted at the front of the vehicle to illuminate the road ahead during nighttime or low-visibility conditions. Modern headlights use various technologies like halogen, LED, or xenon bulbs to provide optimal illumination.
#9. Fog Lights
Fog lights are auxiliary lights mounted low on the front bumper, designed to improve visibility in foggy or heavy rain conditions. They are positioned lower to the ground to shine under the fog, reducing glare and illuminating the road edge.
#10. Signal Lights (Indicator Lights or Turn Signals)
Signal lights, also known as indicator lights or turn signals, are flashing lights at the front and rear of the car. They are used to indicate the driver’s intention to turn or change lanes, crucial for safe maneuvering. They also function as hazard lights when all are activated simultaneously to warn of a vehicle hazard.
#11. Fenders
Fenders (or wings in British English) are body panels that surround the wheel wells. Their primary purpose is to prevent road debris, water, and mud from being thrown up by the tires onto the car body or into the air. Fenders contribute to the car’s aerodynamics and protect other parts from damage.
Side and Rear Exterior Components
The sides and rear of the car complete the exterior profile and incorporate essential safety and functional elements.
#12. Doors (Exterior Details)
Beyond their basic function, door exteriors include components like door handles for opening and closing, side mirrors for rear visibility, and sometimes side skirts for aerodynamic styling. Door panels form the outer skin of the door and contribute to the car’s overall design.
#13. Rear Bumper
Similar to the front bumper, the rear bumper protects the rear of the vehicle from low-speed impacts. It also often houses taillights and sometimes parking sensors. Rear bumpers are designed to protect the trunk and exhaust system components.
#14. Taillights
Taillights are located at the rear of the vehicle and serve multiple functions: indicating the car’s presence to drivers behind, signaling when the brakes are applied (brake lights), and indicating when reversing (reverse lights). They are crucial for rear-end visibility and safety.
#15. Trunk/Decklid
The trunk, also known as the decklid or boot in some regions, is the hinged cover that provides access to the vehicle’s storage compartment at the rear. Trunks vary in size and design depending on the vehicle type, from sedans to SUVs and hatchbacks.
#16. Quarter Panels
Quarter panels are body panels located between the rear door and the trunk, extending around the rear wheel well. They form a significant portion of the car’s side and rear profile and are often styled to integrate seamlessly with the doors and trunk.
#17. Mud Flaps
Mud flaps, also called splash guards, are fitted behind the wheels, especially the rear wheels. They are designed to further prevent mud, stones, and water from being sprayed upwards and backwards by the rotating tires, protecting the vehicle’s undercarriage and following vehicles.
#18. Mirrors (Side and Rearview)
Side mirrors are mounted on the doors and provide the driver with a view of the sides and rear of the vehicle, essential for lane changes and parking. The rearview mirror is mounted inside the cabin and provides a direct view behind the vehicle through the rear window.
#19. Wiper System (Exterior Components)
While the wiper motor is often under the hood, the windshield wipers themselves and their arms are prominent exterior parts. They are responsible for clearing rain, snow, and debris from the windshield to maintain clear visibility for the driver.
#20. Wheels and Hubcaps
Wheels are the circular components that allow the car to move. They are made of metal alloys and fitted with tires. Hubcaps or wheel covers are decorative covers that fit over the center of the wheel, enhancing appearance and sometimes providing aerodynamic benefits.
#21. License Plate Area
The license plate area is a designated space on the front and rear of the vehicle for mounting license plates. It typically includes brackets and lighting to ensure the plate is visible and legally compliant.
Additional Exterior Elements
Beyond the main panels, several other components contribute to the car’s exterior functionality and aesthetics.
#22. Body Kits
Body kits are aftermarket modifications that consist of replacement body panels or additions designed to alter the car’s appearance, often for a sportier or more aggressive look. They can include front and rear bumpers, side skirts, spoilers, and hood scoops.
#23. Body Trim
Body trim refers to decorative elements added to the exterior of the car, such as chrome strips, moldings, or accents. Trim enhances the visual appeal and can define different vehicle trims or models.
#24. Bumper Guards
Bumper guards are protective accessories attached to bumpers to provide extra protection against scratches and minor impacts, particularly in parking situations.
#25. Sunroof
A sunroof is a movable panel in the car’s roof that can be opened to allow light and fresh air into the cabin. Sunroofs can be manually operated or power-driven and come in various sizes and styles.
Car Exterior Parts Diagram
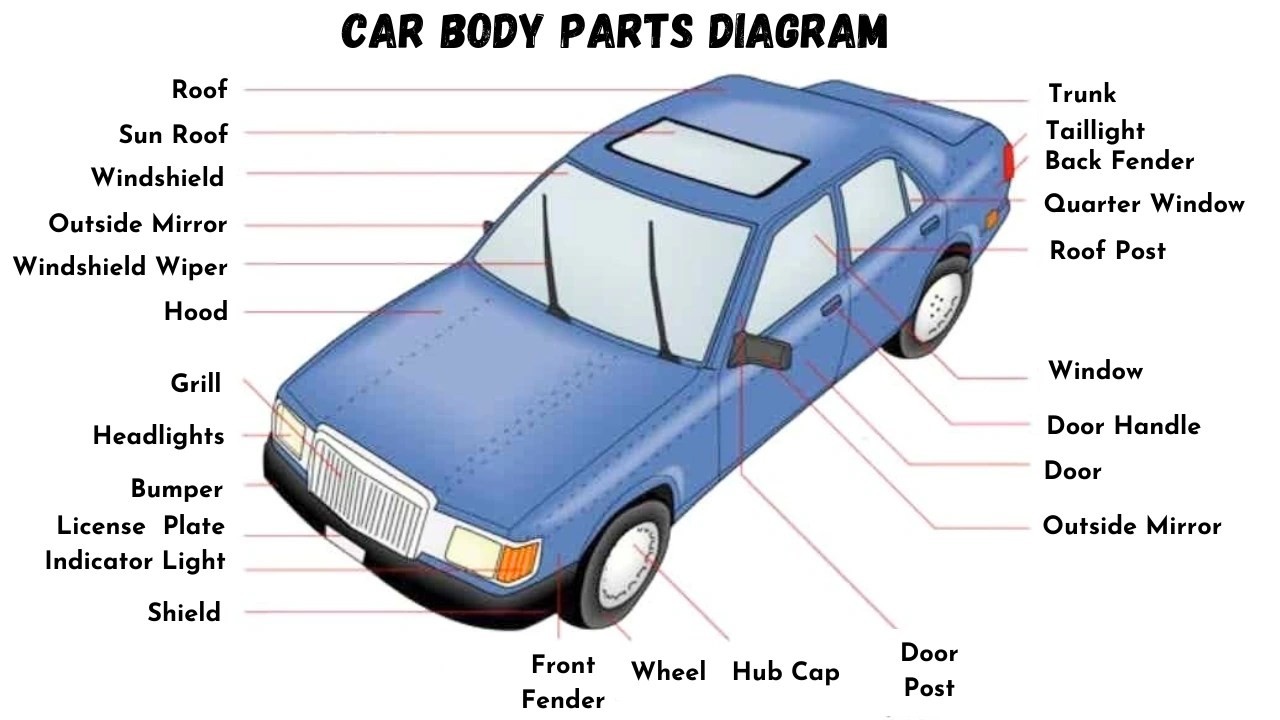{width=1280 height=720}Alt text: Detailed car exterior parts diagram illustrating and labeling major components like bumper, hood, headlights, grille, windshield, roof, doors, wheels, and taillights for easy vehicle anatomy understanding.
Conclusion
Understanding the car exterior parts diagram and the function of each component is beneficial for car owners and enthusiasts alike. This knowledge empowers you to better maintain your vehicle, communicate effectively with mechanics, and appreciate the engineering and design that goes into every car. By familiarizing yourself with these exterior elements, you gain a deeper connection to your vehicle and the automotive world.
