Just like the human body has different parts that work together, a car is also composed of various body parts essential for its function and appearance. Have you ever wondered about the names of these car parts and their roles? As a car expert at cardiagxpert.com, I’m here to guide you through the major components of a car body, not just naming them but also explaining what each part does. This comprehensive guide, complete with a car body parts diagram, will enhance your understanding of automotive anatomy.
Exploring the Main Car Body Parts
Here’s a detailed list of the primary car body parts, which we will explore further in this article:
- Body Shell
- Hood (Bonnet)
- Front Bumper
- Rear Bumper
- Bumper Grille
- Crash Guard (Bullbar)
- Headlight
- Fog Lamp
- Indicator Lights (Signal Lights)
- Wiper Blade
- Radiator
- Radiator Supports
- Cowl Panel
- Quarter Panel
- Fender
- Fender Liners
- Roof
- Sunroof
- Mirrors
- Doors
- Door Handle
- Window Glass
- Quarter Window
- Trunk (Decklid)
- Mud Flaps
- Wheels
- Hubcap
- Dashboard
- Number Plate (License Plate)
- Taillights
Car Body Parts Diagram for Easy Identification
To help you visualize and identify these parts, here is a car body parts diagram:
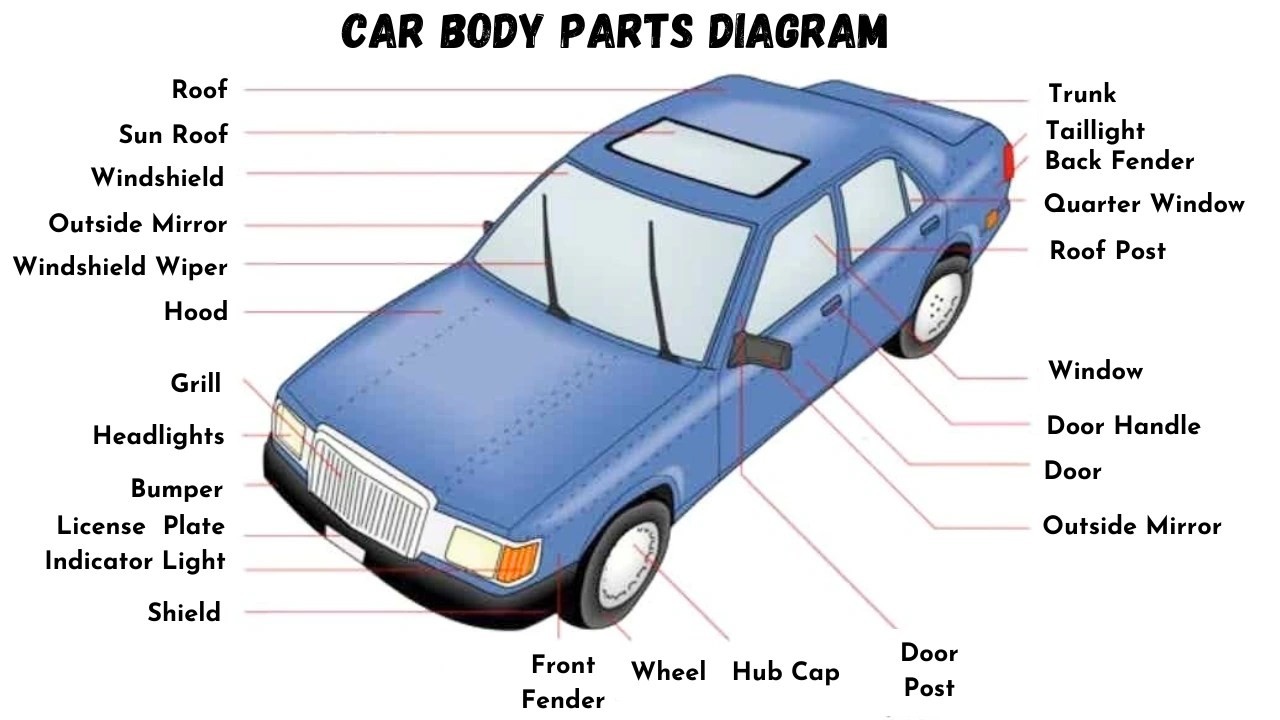 Car Body Parts Diagram
Car Body Parts Diagram
Alt text: Car body parts diagram with names, showcasing the exterior components of a vehicle including bumper, hood, headlights, windshield, roof, doors, wheels, and taillights.
Understanding the Function of Each Car Body Part
Let’s delve deeper into each of these car body parts to understand their function and importance.
#1. Body Shell: The Foundation
The body shell is essentially the main structure or frame of the car. Think of it as the skeleton of the vehicle. It’s the foundational component upon which all other parts are attached, including the engine, chassis, and interior. The body shell provides structural integrity and defines the overall shape of the car. It excludes detachable parts like doors, windows, and interior fittings.
#2. Hood/Bonnet: Protecting the Engine
The hood, also known as the bonnet in some regions, is the hinged cover at the front of the car that protects the engine compartment. It shields the engine and related components from weather elements like rain, snow, and debris. Beyond protection, the hood allows easy access to the engine for maintenance and repairs. Typically made of steel or aluminum, aftermarket options can include lighter materials like carbon fiber for performance vehicles. A latch secures the hood, often released from inside the car for safety.
#3. Front Bumper: Impact Absorption
The front bumper is a crucial safety component designed to absorb impact during low-speed collisions. Positioned at the front of the car, it’s engineered to prevent or minimize damage to the body shell in minor accidents. Bumpers are typically constructed from energy-absorbing materials and often wrap around the corners of the vehicle, integrating with the wheel arches for added protection.
#4. Rear Bumper: Rear-End Protection
Similar to the front bumper, the rear bumper protects the back of the car in collisions. It also often houses the taillights and is designed to safeguard the trunk and exhaust system from damage, especially in low-speed rear-end impacts. Both front and rear bumpers are vital for reducing repair costs and enhancing vehicle safety.
#5. Bumper Grille: Engine Cooling and Aesthetics
The bumper grille is located at the front of the car, usually between the headlights. Often featuring a mesh design, it’s primarily functional, allowing air to flow into the engine bay to cool the engine and radiator. Different types of grilles exist, including main grilles, lower grilles, and fog light grilles, each designed to optimize airflow and complement the car’s styling. Grille designs are vehicle-specific, making it essential to choose the correct one for your car model if replacing it.
#6. Crash Guards/Bullbars: Enhanced Front Protection
Crash guards, or bullbars, are metal bars typically mounted to the front (and sometimes rear) of a vehicle. They offer extra protection to the bumper and front body in collisions, especially in off-road driving or areas with potential animal crossings. While providing robust protection, their legality and pedestrian safety implications can vary by region.
#7. Headlight: Illuminating the Road Ahead
Headlights are essential lighting components mounted at the front of the car. Their primary function is to illuminate the road ahead, ensuring safe driving at night or in low-visibility conditions. Modern headlights come in various types, including halogen, LED, and xenon, each offering different levels of brightness and efficiency.
#8. Fog Lamp: Improved Visibility in Poor Weather
Fog lamps are specialized lights designed to improve visibility in adverse weather conditions like fog, heavy rain, or snow. Positioned lower than headlights, they cut through fog and mist more effectively by directing light downwards, reducing glare and illuminating the road closer to the ground.
#9. Signal Lights/Indicator Lights: Communicating Turns
Signal lights, also known as indicator lights or turn signals, are located at the front and rear of the car. When activated, they blink to indicate the driver’s intention to turn or change lanes, crucial for safe maneuvering and communication with other drivers. Emergency lights, which activate all signal lights simultaneously, are used to warn other drivers of hazards.
#10. Roof and Pillars: Structural Support and Protection
The roof forms the upper covering of the car, protecting occupants from the elements. Pillars are the vertical supports that hold up the roof, adding significant structural rigidity to the vehicle. They contribute to the car’s overall strength and safety, particularly in rollover accidents. Cars have different numbers and configurations of pillars (A, B, C, and sometimes D-pillars), depending on their design and size.
#11. Doors and Windows: Entry, Exit, and Weather Protection
Doors provide access to the car’s interior, allowing passengers to enter and exit. They also offer side impact protection and house components like door locks, windows, and speakers. Windows, fitted into the doors and body, protect occupants from wind, rain, and external elements while providing visibility. Car windows, unlike the fixed windshield, can usually be lowered and raised.
#12. Rear Panels: Housing Rear Components
Rear panels encompass the rear section of the car’s body, including taillights, the trunk lid (decklid or tailgate), and the rear bumper. They also often incorporate the rear window and contribute to the vehicle’s aerodynamic profile. Rear quarter panels, specifically, are located between the rear door and the trunk.
#13. Front Panels: Housing Front Components
Front panels constitute the forward section of the car’s body, housing the headlights, grille, front bumper, and fenders. They are designed for both aesthetics and functionality, influencing the car’s appearance and aerodynamic efficiency. Fenders, which cover the wheel wells, are also part of the front panels.
#14. Steering Wheel and Car Wheels: Control and Mobility
While the steering wheel is an interior component, it’s integral to the car’s body system as it controls the direction of the car’s wheels. The wheels themselves are exterior body parts, responsible for the car’s mobility and contact with the road. They are connected to the chassis and steering system, enabling the car to move and be controlled.
#15. Mirrors and Windows: Visibility and Awareness
Mirrors, including rearview and side mirrors, are crucial for driver awareness, providing visibility of the surroundings and reducing blind spots. Windows, especially the windshield and side windows, are essential for forward and peripheral vision, ensuring safe driving by allowing the driver to see the road and other vehicles. Windshield wipers are also part of this system, maintaining clear visibility in rain or snow.
#16. Bearings: Smooth Wheel Rotation
Wheel bearings are critical components within the wheel assembly that connect the wheel to the axle. They enable the wheels to rotate smoothly and freely, reducing friction and ensuring efficient movement. Damaged wheel bearings can cause noise and affect handling.
#17. Body Kits: Customization and Aerodynamics
Body kits are sets of aftermarket body parts designed to modify a car’s appearance and sometimes improve aerodynamics. They typically include front and rear bumpers, side skirts, spoilers, and sometimes hood scoops. Body kits allow for vehicle customization and can enhance visual appeal or performance.
#18. Body Trim: Decorative Elements
Body trim refers to decorative elements attached to the exterior and interior of a car to enhance its aesthetic appeal. This can include chrome strips, moldings, and other accents that refine the vehicle’s look.
#19. Bumper Guards: Scratch and Scrape Protection
Bumper guards are protective accessories designed to shield bumpers from scratches and scrapes, especially in parking situations or minor impacts. They offer an additional layer of protection to the bumper’s surface, maintaining its appearance.
#20. Cabin Parts: Interior Components
Cabin parts refer to the interior components of the car’s body, including the dashboard, seats, door panels, and headliner. While not exterior parts, they are integral to the overall car body and passenger comfort.
#21. Cables: Electrical Connections
Cables are the wiring system of the car, connecting electrical components to the battery and power source. While not visible exterior parts, they are essential for powering lights, signals, and other electrical systems within the car body.
#22. Coolant Bottle/Reservoir: Engine Cooling System
The coolant reservoir, or coolant bottle, is a container in the engine compartment that holds coolant for the engine’s cooling system. It accommodates the expansion and contraction of coolant as the engine heats and cools, maintaining proper coolant levels.
#23. Dashboard: Vehicle Control and Information
The dashboard, also known as the instrument panel, is located inside the car, in front of the driver. It houses instruments and controls for operating the vehicle, including the speedometer, fuel gauge, and warning lights, providing essential information to the driver.
#24. Fenders: Wheel Arch Coverage
Fenders are the body panels that frame the wheel arches, covering the wheels. Their primary purpose is to prevent road debris, mud, water, and stones from being thrown up by the tires, protecting the car’s body and other vehicles on the road.
#25. License Plate and Brackets: Vehicle Identification
The license plate, or number plate, is a metal plate attached to the front and rear of the vehicle, displaying the car’s registration number. Brackets securely hold the license plates in place, ensuring legal vehicle identification.
#26. Mud Flaps/Mudguards: Protecting the Undercarriage
Mud flaps, also called mudguards or splash guards, are fitted behind the wheels, particularly the rear wheels. They prevent mud, dirt, and road spray from hitting the undercarriage of the vehicle, reducing corrosion and keeping the car cleaner.
#27. Quarter Panels: Side Body Sections
Quarter panels are body panels located between the rear door and the trunk, wrapping around the rear wheel well. They form a significant part of the car’s side body structure and contribute to its styling.
#28. Sunroof: Natural Light and Ventilation
A sunroof is a movable panel in the car roof that can be opened to allow light and fresh air into the passenger compartment. Sunroofs can be manually or electrically operated and come in various designs, enhancing the driving experience.
#29. Wheel Rim: Tire Mounting Edge
The wheel rim is the outer edge of the wheel, onto which the tire is mounted. It’s the structural component that holds the tire securely and forms the visible outer part of the wheel.
#30. Windshield Washer Motor: Cleaning the Windshield
The windshield washer motor powers the windshield washer system, pumping washer fluid from the reservoir to the windshield. It ensures the windshield can be cleaned of dirt and debris for clear visibility.
#31. Wiper: Clearing the Windshield
Wipers are devices that sweep across the windshield to remove rain, snow, and debris, maintaining clear visibility for the driver in inclement weather. They are crucial safety components, especially in rain and snow.
FAQs about Car Body Parts
What are the main body parts of a car?
The main body parts include the body shell, hood, bumpers, fenders, roof, doors, and trunk. These are the primary structural and protective components defining the car’s form and function.
What are car panels called?
Car panels have specific names depending on their location. The front panels include the hood and fenders. The side panels include doors and quarter panels. The rear panels include the trunk lid and rear fenders. The roof is the top panel.
What is the most important part of a car?
While many parts are critical, the chassis is often considered the main part of a car. It provides the structural framework for all other components, including the suspension, axles, and wheels.
How do I identify a car part?
To identify a car part correctly, you can use the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN), a unique code specific to your car. You can also look for part codes directly on the component itself. Consulting a car parts diagram can also be very helpful for visual identification.
What is the front body of a car called in British English?
In British English, the front body part of a car that covers the engine is called the bonnet. In American English, it is referred to as the hood.
By understanding the names and functions of these car body parts, you’ll be better equipped to maintain your vehicle, communicate with mechanics, and appreciate the complex engineering that goes into automotive design. Use this guide and the car body parts diagram as your reference for all things related to car anatomy!
