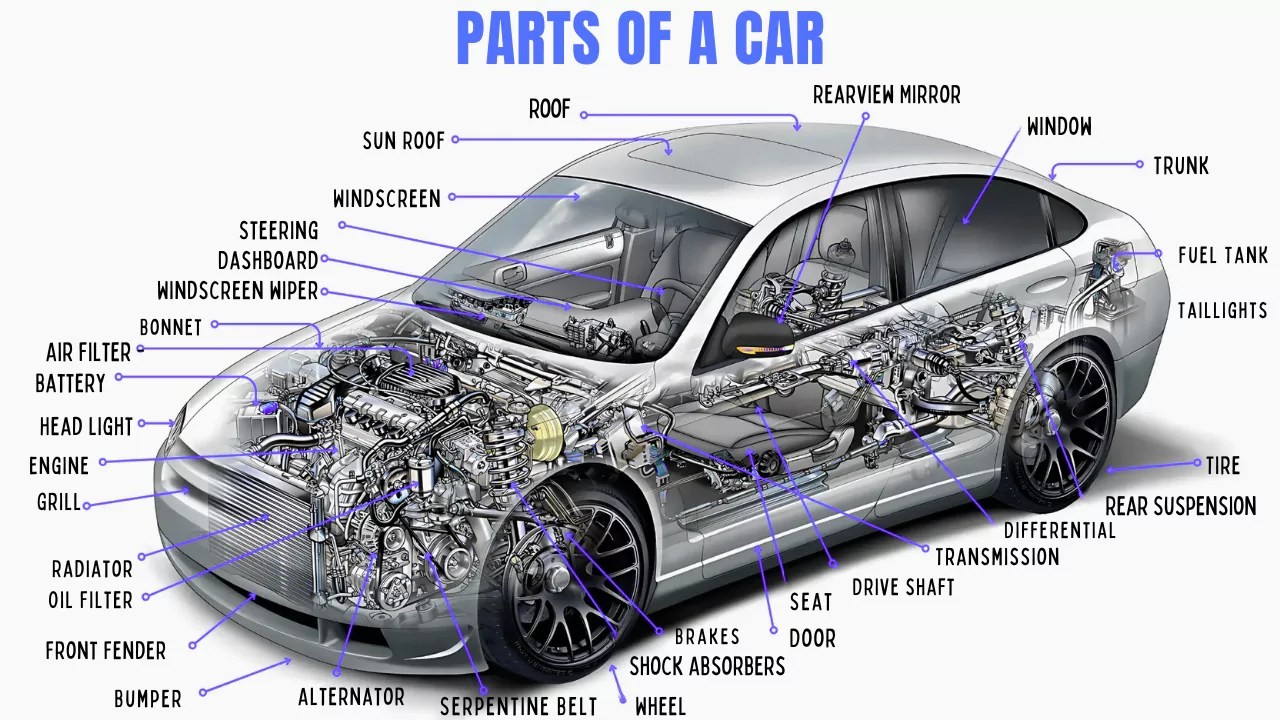
Understanding the intricate workings of your vehicle can often feel like navigating a complex maze. A car is composed of numerous parts, each playing a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient operation. While you don’t need to be a master mechanic, familiarizing yourself with the basic components of your car is incredibly beneficial. This knowledge empowers you to be a more informed driver, communicate effectively with automotive technicians, and better understand your vehicle’s needs.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the anatomy of a car. We will explore various car parts, providing clear names and illustrative pictures to enhance your understanding. Whether you’re a seasoned car enthusiast or a new driver, this article will serve as your ultimate resource to learn about “Car All Parts Name With Picture”.
Exterior Car Parts Names
The exterior of your car is the first line of defense against the elements and contributes significantly to its safety and aesthetics. Let’s explore some key exterior components:
Seat Belt
Seat belts are crucial safety restraints designed to secure occupants against harmful movement during a collision or sudden stop. They work by distributing the force of impact across the stronger parts of the body, preventing ejection and minimizing injury.
Headlights
Headlights are powerful lamps located at the front of the vehicle, essential for illuminating the road ahead during nighttime or low-visibility conditions. They significantly improve driving safety by enhancing visibility for the driver and making the vehicle more visible to other road users.
Taillights
Taillights are red lights positioned at the rear of the vehicle, making it visible to drivers approaching from behind, especially in darkness or poor weather. They are crucial for preventing rear-end collisions and ensuring safe driving.
Indicator Lights
Indicator lights, also known as turn signals or blinkers, are flashing lights on the front, sides, and rear of a vehicle. They signal the driver’s intention to turn or change lanes, promoting safe maneuvering and communication with other drivers.
Windshield
The windshield, or windscreen, is the front window of a vehicle, typically made of laminated safety glass. It provides a clear field of vision for the driver while protecting occupants from wind, debris, and weather elements.
Windshield Wipers
Windshield wipers are mechanical arms with rubber blades designed to sweep across the windshield, removing rain, snow, and debris to maintain clear visibility for the driver in inclement weather.
Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors are electronic devices used in modern vehicles to detect the presence of nearby objects. They are often integrated into parking assist systems and safety features, alerting the driver to obstacles to prevent collisions.
Car Hood
The car hood, or bonnet, is the hinged cover over the engine compartment in front-engine vehicles. It provides access to the engine for maintenance and repairs, and also protects the engine components from external elements.
Trunk
The trunk, or boot, is the primary storage compartment in the rear of most sedans, coupes, and convertibles. It is designed to carry luggage, cargo, and other items securely separated from the passenger cabin.
Wheel/Tire
Wheels are the circular components that tires are mounted on, enabling the car to roll. Tires are rubber coverings fitted around the wheels, providing traction, cushioning, and grip for driving, braking, and steering.
License Plate/Bumper Stickers
The license plate is a mandatory identification tag attached to the exterior of a vehicle, registered with a governing authority. Bumper stickers are decorative or expressive decals that individuals may choose to apply to their vehicle’s bumper.
Interior Car Parts Names
The interior car parts are all about driver control, passenger comfort, and accessing important information about the vehicle’s operation. Let’s look at some key components inside the car:
Fuel Gauge
The fuel gauge is an instrument that indicates the amount of fuel remaining in the vehicle’s fuel tank. It allows the driver to monitor fuel levels and plan for refueling accordingly, preventing unexpected fuel depletion.
Speedometer
A speedometer is a gauge that displays the instantaneous speed of the vehicle, usually in miles per hour (MPH) or kilometers per hour (km/h). It is crucial for drivers to monitor their speed and adhere to speed limits for safe driving.
Temperature Gauge
The temperature gauge indicates the temperature of the engine coolant. It helps drivers monitor the engine’s operating temperature to prevent overheating, which can cause serious engine damage.
Odometer
An odometer is an instrument that records the total distance traveled by a vehicle. It provides a cumulative mileage reading, useful for tracking vehicle usage, maintenance intervals, and resale value.
RPM Gauge
The RPM gauge, or tachometer, displays the engine’s rotation speed in revolutions per minute (RPM). It helps drivers understand engine performance and shift gears at optimal RPM ranges, especially in manual transmission vehicles.
Cruise Control
Cruise control is a system that automatically maintains a constant vehicle speed set by the driver. It is primarily used for comfortable long-distance driving on highways, reducing driver fatigue.
Gear Shift
The gear shift, or gear selector, is a lever used to change gears in a manual or automatic transmission vehicle. In manual cars, it’s also known as a stick shift, while in automatics, it selects driving modes like Park, Drive, and Reverse.
Airbags
Airbags are safety cushions designed to inflate rapidly in the event of a collision. They provide supplementary protection to seat belts, reducing the risk of injury by cushioning the occupant’s body during a crash.
Steering Wheel
The steering wheel is the primary control for steering the vehicle. By turning the wheel, the driver controls the direction of the front wheels, allowing for maneuvering and navigation. Modern steering wheels often integrate controls for audio, cruise control, and other vehicle functions.
Engine and Mechanical Car Parts Names
Beneath the car’s body lies a complex network of mechanical systems that power and control the vehicle. Understanding these parts is essential for grasping how a car operates:
Engine System
The engine is the heart of the car, converting fuel into mechanical power.
Engine
The engine, or motor, is the power plant of a vehicle. In most cars, it’s an internal combustion engine (ICE) that burns fuel to generate power. Electric vehicles (EVs) utilize electric motors powered by batteries.
Piston
Pistons are cylindrical components that move up and down within the engine cylinders. The combustion of fuel pushes the pistons, converting chemical energy into mechanical motion.
Crankshaft
The crankshaft is a rotating shaft that converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotary motion. This rotational force is then transmitted to the transmission and eventually to the wheels.
Camshaft
The camshaft is a rotating shaft with lobes that control the opening and closing of the engine’s valves. Precise valve timing is crucial for efficient engine operation and combustion.
Combustion Chamber
The combustion chamber is the space within the cylinder where the air-fuel mixture is compressed and ignited. This controlled explosion generates the power that drives the pistons.
Timing Belt
The timing belt is a toothed belt that synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft. It ensures that the engine valves open and close in coordination with the piston movement for proper combustion.
Serpentine Belt
The serpentine belt is a long, winding belt that drives multiple engine accessories, such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. It efficiently transfers power from the engine’s crankshaft.
Air Filter
The air filter cleans the air entering the engine, removing dust, dirt, and debris. Clean air is essential for efficient combustion and prevents damage to engine components.
Ignition System
The ignition system is responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in gasoline engines. It includes the ignition coil, spark plugs, and related wiring, generating the spark needed for combustion.
Spark Plug
Spark plugs are components of the ignition system that generate a spark within the combustion chamber. This spark ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture, initiating the power stroke of the engine.
Fuel Pump
The fuel pump is responsible for drawing fuel from the fuel tank and delivering it to the engine at the required pressure. It ensures a constant supply of fuel for combustion.
Fuel Tank
The fuel tank is the storage container for the vehicle’s fuel, typically gasoline or diesel. It is designed to safely store fuel and supply it to the engine as needed.
Lubrication System
The lubrication system circulates engine oil to reduce friction between moving parts. This lubrication minimizes wear and tear, dissipates heat, and helps keep the engine running smoothly.
Cooling System
The cooling system prevents the engine from overheating.
Radiator
The radiator is a heat exchanger that cools the engine coolant. Hot coolant from the engine flows through the radiator, and air passing through the radiator fins dissipates the heat, maintaining optimal engine temperature.
Water Pump
The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine and cooling system. It ensures continuous coolant flow to remove heat from the engine block and cylinder head, preventing overheating.
Cooling System
The engine cooling system is a network of components that regulate engine temperature. It includes the radiator, water pump, thermostat, hoses, and coolant, working together to prevent overheating and maintain efficient engine operation.
Temperature Gauge
As mentioned earlier in interior parts, the temperature gauge, while displayed inside, is fundamentally linked to the engine’s cooling system, providing critical temperature information to the driver.
Transmission System
The transmission system transfers power from the engine to the wheels.
Transmission
The transmission is a crucial component that manages the power flow from the engine to the wheels. It allows the engine to operate efficiently across a range of speeds and loads through gear changes. Transmissions can be manual or automatic.
Clutch
The clutch is used in manual transmission vehicles to temporarily disconnect the engine from the transmission. This disengagement allows the driver to change gears smoothly.
Torque Converter
The torque converter is a fluid coupling in automatic transmissions that transmits engine power to the transmission. It allows the engine to continue running when the vehicle is stopped and provides torque multiplication for smooth acceleration.
Gear Shift
While we listed the gear shift in interior parts for its driver interface aspect, its primary function is to control the transmission gears, making it a vital part of the transmission system. Different gear positions enable forward motion, reverse, and neutral.
Propeller Shaft/Driveshaft
The propeller shaft, or driveshaft, transmits rotational power from the transmission to the differential, especially in rear-wheel-drive and four-wheel-drive vehicles. It is a rotating component that bridges the distance between the transmission and axles.
Differential
The differential is a gear mechanism that allows the wheels on the same axle to rotate at different speeds when the vehicle turns. This is essential for smooth cornering, preventing wheel slippage and driveline stress.
Axle (Front and Rear)
Axles are shafts that connect the wheels to the differential and support the vehicle’s weight. They transmit power to the wheels, causing them to rotate. Cars have front and rear axles, depending on the drive configuration.
Steering and Suspension System
These systems control the handling and ride comfort of the car.
Steering System
The steering system enables the driver to control the direction of the vehicle. It typically involves the steering wheel, steering column, and steering gear, which translates the driver’s input into wheel movement.
Front Steering and Suspension
The front steering and suspension system combines steering components with the front suspension. It allows for both steering control and cushioning of road shocks at the front wheels, contributing to handling and ride comfort.
Rear Suspension
The rear suspension system supports the rear of the vehicle and absorbs road shocks at the rear wheels. It works in conjunction with the front suspension to provide a stable and comfortable ride.
Shock Absorber
Shock absorbers, or dampers, control the movement of the suspension springs. They dampen oscillations, preventing excessive bouncing and ensuring the tires maintain contact with the road for better control.
Braking System
The braking system is crucial for safety, allowing the car to stop.
Brakes (Disc and Drum)
Brakes are essential safety components that slow down or stop the vehicle. Common types are disc brakes and drum brakes, which use friction to convert kinetic energy into heat, thus halting the car’s motion. Disc brakes are generally more effective and are often used on the front wheels, while drum brakes may be used on the rear.
Exhaust System
The exhaust system manages and treats engine exhaust gases.
Exhaust System
The exhaust system routes exhaust gases away from the engine, reduces noise, and treats harmful pollutants. It includes components like the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, resonator, and tailpipe.
Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is an emission control device that reduces harmful pollutants in the exhaust gases. It uses chemical reactions to convert hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances.
Muffler
The muffler is a component in the exhaust system designed to reduce engine noise. It uses chambers and baffles to reflect and cancel out sound waves, making the vehicle quieter.
Resonator
The resonator is often used in conjunction with the muffler to further refine exhaust sounds. It targets specific frequencies to eliminate droning noises, enhancing the exhaust note.
Tailpipe
The tailpipe is the final section of the exhaust system, where the treated exhaust gases are discharged into the atmosphere, away from the vehicle cabin.
O2 Sensor
The O2 sensor, or oxygen sensor, measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. This information is sent to the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize the air-fuel mixture for efficient combustion and emission control.
Electrical System
The electrical system powers various functions in the car.
Battery
The battery provides the initial electrical power to start the engine and operate electrical accessories when the engine is off. It is a rechargeable energy storage device crucial for the car’s electrical system.
Alternator
The alternator is a generator driven by the engine that recharges the battery and supplies electrical power to the car’s electrical systems while the engine is running. It keeps the battery charged and powers electrical components.
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
The electronic control unit (ECU), or engine control unit, is a computer that manages various electronic systems in the car, including engine management, transmission control, and safety features. It optimizes vehicle performance and efficiency.
Other Important Car Parts Names
Powertrain
The powertrain encompasses all the components that generate power and transmit it to the wheels, making the car move. It includes the engine, transmission, driveshaft, axles, and differential, working together to propel the vehicle.
FAQs
What is the basic part of a car?
The basic parts of a car are often considered to be the engine, transmission, chassis, and body. However, essential operational components include the engine, gearbox, clutch (if manual), battery, brakes, radiator, steering, and suspension. These are fundamental for a car to function as a vehicle.
What is the main part of a car?
The engine is arguably the main part of a car, as it is the source of power. Without an engine, a car cannot move on its own. It converts fuel into mechanical energy, which is then used to drive the wheels.
What are the two main parts of a car?
From a structural perspective, the two main parts could be considered the chassis or frame and the body. The frame provides the structural support, while the body encloses the components and provides the shape of the car. Functionally, one could argue the engine and transmission as the two main parts for mobility.
How many car parts are in a car?
The number of parts in a car is substantial. It is estimated that a typical car has around 30,000 parts, ranging from major components like the engine and transmission to small nuts, bolts, and electronic components. This number can vary depending on the complexity and model of the vehicle.
By understanding these car all parts name with picture, you are now better equipped to appreciate the complexity and engineering that goes into every vehicle on the road. This knowledge will not only make you a more informed car owner but also enhance your understanding of basic automotive mechanics.