Just like the human body has different parts that work together, a car is also composed of numerous components. Understanding these parts is crucial for car owners and enthusiasts alike. Have you ever wondered about the specific names of each section of your vehicle? In this article, we’ll explore the essential components of a car, focusing particularly on the back part and what it’s called, enhancing your understanding of automotive anatomy.
Car Body Parts: An Overview
The exterior of a car is made up of various body parts, each serving a specific function and contributing to the vehicle’s overall structure and aesthetics. These parts range from safety components to elements that enhance the car’s appearance. Let’s delve into a list of common car body parts:
- Body shell
- Hood (Bonnet)
- Front bumper
- Rear bumper
- Bumper grille
- Crash guard (Bullbar)
- Headlight
- Fog lamp
- Indicator lights (Signal lights)
- Wiper blades
- Radiator
- Radiator supports
- Cowl panel
- Quarter panel
- Fender
- Fender liners
- Roof
- Sunroof
- Mirrors
- Doors
- Door handle
- Window glass
- Quarter window
- Trunk (Decklid)
- Mud flaps
- Wheels
- Hubcap
- Dashboard
- Number plate (License plate)
- Taillights
Visualizing Car Body Parts
To better understand the location and arrangement of these parts, refer to the car body parts diagram below. This visual representation will help you identify each component discussed in this article.
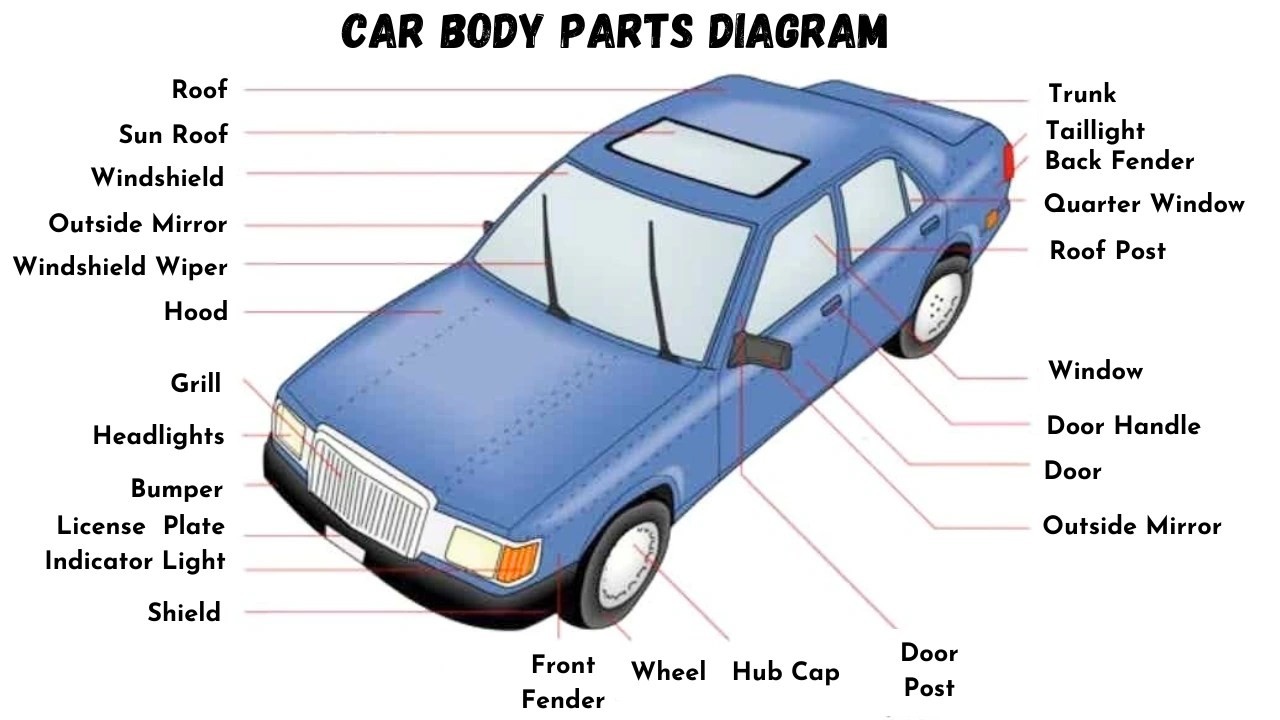 Car Body Parts Diagram
Car Body Parts Diagram
Decoding the Car Body Parts
Let’s explore each of these car body parts in detail, understanding their function and significance.
#1. Body Shell: The Foundation
The body shell is essentially the main structure of the car. It’s the foundational framework upon which all other components are attached. Think of it as the skeleton of the car, excluding doors, windows, and interior fittings. The engine, mechanical, and electrical systems are all housed within or attached to the body shell. It provides structural integrity and defines the overall shape of the vehicle.
#2. Hood/Bonnet: Engine Bay Cover
The hood, also known as the bonnet in some regions, is the hinged cover at the front of the car. It sits directly over the engine bay in front-engine vehicles. Its primary functions are twofold: protection and accessibility. The hood shields the engine and its associated components from weather elements, road debris, and accidental damage. Simultaneously, it provides easy and safe access to the engine compartment for routine maintenance and repairs. Typically made of steel or aluminum for strength and lightness, aftermarket options can include materials like carbon fiber for enhanced performance or aesthetics. A latch, often concealed and released from inside the car, secures the hood.
#3. Front Bumper: Impact Absorption in the Front
The front bumper is a crucial safety component mounted at the front of the vehicle. Its main purpose is to absorb impact during low-speed collisions, protecting the car’s body and occupants. Extending across the front width of the car, it often wraps around the front corners, partially covering the wheel arches for the front wheels. Bumpers are designed to cushion impacts with other vehicles or objects, minimizing damage in minor accidents.
#4. Rear Bumper: Protecting the Back Part of the Car
Mirroring the function of the front bumper, the rear bumper provides protection to the back part of the car. It safeguards the rear of the vehicle in collisions, housing taillights and protecting the trunk, exhaust system, and other rear components from damage, especially in low-speed impacts. Both front and rear bumpers are essential for minimizing repair costs and enhancing vehicle safety.
#5. Bonnet Grill: Engine Cooling and Style
Located between the headlights, the bonnet grill is a distinctive trim piece, often featuring a mesh design. While it adds to the car’s aesthetic appeal, its primary function is practical: engine cooling. As the car moves, air flows through the grille, providing ventilation to the engine bay and preventing overheating. Grille designs vary significantly between car models and brands. Different types include main grilles, lower grilles, and fog grilles. When replacing a grille, ensuring compatibility with your specific vehicle model is crucial for proper fit and function.
#6. Bullbars or Crash Guards: Extra Protection
Bull bars, also known as crash guards, are robust metal grills typically mounted to the front or rear of a vehicle. Designed for heavy-duty protection, they are intended to minimize damage to the vehicle’s body in collisions, particularly in off-road or rural environments where impacts with animals or debris are more likely.
#7. Headlight: Illuminating the Road Ahead
Headlights, or headlamps, are essential for safe driving at night and in low-visibility conditions. Mounted at the front of the vehicle, they project a beam of light to illuminate the road ahead, allowing the driver to see obstacles and navigate safely. While “headlight” and “headlamp” are often used interchangeably, “headlamp” technically refers to the device itself, while “headlight” refers to the beam of light it produces.
#8. Fog Lamp: Enhancing Visibility in Poor Weather
Fog lamps are specialized lights designed to improve visibility in adverse weather conditions like fog, heavy rain, or dust storms. Typically mounted lower than headlights, front fog lights are positioned to cut through the mist and illuminate the road surface directly ahead, enhancing the driver’s view of the road edges and markings.
#9. Signal Lights: Communicating Intentions
Signal lights, or indicator lights, are a set of blinking lights located at the front and rear of the car. Their purpose is to communicate the driver’s intended direction to other road users. Activating the signal lever, usually found on the steering wheel column, causes the lights on the corresponding side of the car to blink, indicating an intention to turn or change lanes. Modern vehicles also feature hazard lights, which activate all signal lights simultaneously to warn other drivers of a potential hazard or emergency.
#10. Roof and Pillars: Structural Support and Protection
The roof forms the upper enclosure of the car, protecting occupants from the elements – rain, snow, sun, and wind. It’s a critical structural component, contributing to the car’s overall rigidity and safety. Pillars are the vertical support structures that hold up the roof. These beams also enhance the structural integrity of the windshield and upper frame. The number of pillars varies depending on the vehicle’s design and size. Hatchback designs often feature slanted rear pillars for aerodynamic and aesthetic reasons.
#11. Doors and Windows: Access and Weather Protection
Doors provide access to the car’s interior, allowing passengers to enter and exit the vehicle. They also play a crucial role in occupant safety, providing structural protection in side-impact collisions. Car doors consist of various components like door locks, panels, handles, and sometimes storage compartments. The number of doors can vary from two to four depending on the car model. Windows, integrated into the doors and body, protect occupants from the elements. Unlike the fixed windshield, door windows can typically be lowered and raised for ventilation.
#12. Rear Panels: The Back End Components
Rear panels encompass the back part of the car, housing several key components. This area often includes brake lights, taillights, the tailgate or trunk lid, the rear bumper, and parts of the exhaust system. The rear side panels also incorporate the rear doors (if present) and the wheel wells for the rear wheels and suspension components. Understanding the rear panels is key to identifying the Back Part Of The Car Is Called many different things depending on the specific component.
#13. Front Panels: The Face of the Car
Front panels constitute the front section of the car’s body. They house components like the front bumper, grille, headlight assemblies, fenders, fog lights, and turn signals. The design and arrangement of the front panels contribute significantly to the car’s visual identity.
#14. Steering Wheel and Car Wheels: Control and Motion
The steering system, including the steering wheel, steering column, and linkages, allows the driver to control the direction of the car. It connects to the wheels, enabling them to turn as needed. Wheels, along with tires, are essential for vehicle movement. Front wheels also incorporate suspension components for stability and ride comfort.
#15. Front and Rear View Mirrors and Windshield Wipers: Visibility Aids
Mirrors, both interior and exterior, are vital for driver awareness, providing views of the surroundings and minimizing blind spots. Windshield wipers are crucial for maintaining clear visibility in rain, snow, or when the windshield is dirty. Powered by a motor, the wiper system comprises blades, arms, linkages, and a washer fluid reservoir to clean the windshield effectively.
#16. Bearings: Smooth Wheel Rotation
Wheel bearings are integral parts of the wheel assembly, connecting the wheel to the axle. They enable smooth and low-friction rotation of the wheels, contributing to efficient and comfortable driving.
#17. Body Kits: Customization and Aerodynamics
Body kits are sets of aftermarket components designed to modify a car’s exterior appearance and sometimes improve aerodynamics. They typically include front and rear bumpers, side skirts, spoilers, and hood scoops. Body kits allow for vehicle customization and can enhance both style and performance.
#18. Body Trim: Decorative Elements
Car trim refers to decorative elements attached to the interior and exterior of a vehicle to enhance its aesthetic appeal. Trim can be made from various materials like chrome, plastic, or wood, and can be applied to areas like windows, doors, and dashboards.
#19. Bumper Guards: Scratch and Scrape Protection
Bumper guards are protective accessories designed to shield car bumpers from scratches, scrapes, and minor impacts. They are particularly useful in urban environments or tight parking spaces where bumper damage is more likely.
#20. Cabin Parts: Interior Components
Cabin parts refer to all components within the car’s interior, including seats, dashboard, steering wheel, and interior trim. These parts contribute to passenger comfort, convenience, and the overall driving experience.
#21. Cables: Electrical Wiring
Cables are the electrical wiring system of the car, connecting the battery to all electrical components, from lights and sensors to the engine control unit. A reliable cable system is essential for the proper functioning of all electrical systems in the vehicle.
#22. Coolant Bottle: Engine Temperature Regulation
The coolant bottle, or coolant reservoir, is a plastic container located in the engine compartment. It holds the engine coolant, which circulates through the engine to regulate its temperature. The reservoir accommodates the expansion and contraction of coolant as the engine heats up and cools down.
#23. Dashboard: Driver Information and Controls
The dashboard, also called the instrument panel, is located in front of the driver. It houses instruments that display vital information like speed, fuel level, and engine temperature, as well as controls for various vehicle functions.
#24. Fenders: Wheel Arch Liners
Fenders are body panels that frame the wheel arches. Their primary function is to prevent debris like mud, stones, and water from being thrown up by the rotating tires, protecting the car’s body and other vehicles.
#25. License Plate and Brackets: Vehicle Identification
The license plate, or number plate, is a metal or plastic plate attached to the vehicle displaying its official registration number. License plate brackets securely mount the plate to the front and/or back part of the car.
#26. Mud Flaps: Underbody Protection
Mud flaps, also known as mudguards or splash guards, are fitted behind the wheels, especially the rear wheels. They prevent mud, dirt, and road spray from reaching the vehicle’s undercarriage, reducing corrosion and keeping the car cleaner.
#27. Quarter Panels: Between Door and Trunk
Quarter panels are body panels located between the rear door (or only door in two-door models) and the trunk at the back part of the car. They typically wrap around the wheel well and contribute to the car’s side profile and structural integrity.
#28. Sunroof: Natural Light and Airflow
A sunroof is a movable panel in the car’s roof that can be opened to let in natural light and fresh air into the cabin. Sunroofs come in various designs, from manually operated pop-up versions to electrically operated sliding panoramic roofs.
#29. Wheel: Tire Mounting
The wheel is the circular component to which the tire is mounted. It provides the structure to support the tire and connect it to the vehicle’s axle. The rim is the outer edge of the wheel that holds the tire bead.
#30. Windshield Washer Motor: Cleaning the Windshield
The windshield washer motor powers the windshield washer system, pumping washer fluid from the reservoir to the windshield. It is typically located near the washer fluid tank, often in the front part of the car.
#31. Wiper: Rain Removal
Wipers are devices that sweep across the windshield to remove rain, snow, and debris, ensuring clear visibility for the driver in inclement weather.
FAQs about Car Body Parts
What are common names for car body parts?
Common car body part names include:
- Bonnet/Hood: The engine cover.
- Bumper: Front and rear impact protection.
- Cowl Screen: Area below the windshield wipers.
- Decklid/Trunk Lid: Cover for the trunk at the back part of the car.
- Fender/Wing/Mudguard: Wheel arch panel.
- Grille/Grill: Front air intake and styling element.
- Pillar: Roof support structure.
What are car panels often called?
Car panels are generally referred to by their location and function, such as door panels, roof panel, and quarter panels. The front section between the door and the hood is called a fender or front wing. Quarter panels, located at the back part of the car, are also sometimes referred to as rear wings.
What is considered the main part of a car?
The chassis is often considered the main structural part of a car. It includes the frame, suspension system, axles, and wheels, providing the foundation for the entire vehicle.
How can I identify a specific car part?
To identify a car part accurately:
- Use the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): The VIN is unique to your car and can be used to find compatible parts.
- Look for Part Codes: Many parts have a code stamped or printed on them, which can be used for identification.
What is the front part of a car called in British English?
In British English, the front part of a car that covers the engine is called the bonnet. In American English, it is called the hood.
Understanding the names and functions of car body parts, especially the components at the back part of the car, is essential for vehicle maintenance, repair, and general car knowledge. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview to help you become more familiar with your vehicle’s anatomy.