The interior of your car is more than just seats and a steering wheel; it’s your personal space on the road, designed for comfort, convenience, and safety. If you’re an owner of an automatic car, understanding the specific interior parts and their functions becomes even more relevant, as automatic transmissions influence certain aspects of the interior design and features. This comprehensive guide, crafted by the experts at cardiagxpert.com, will delve into the world of Automatic Car Interior Parts, exploring their names, roles, and how they contribute to your driving experience.
Understanding these components is not just about knowing your car better; it’s crucial for informed decision-making when purchasing a vehicle, planning upgrades, or troubleshooting issues. Automatic cars, with their ease of driving, often come equipped with advanced interior features focused on enhancing the driving experience and convenience. Let’s explore these essential parts in detail.
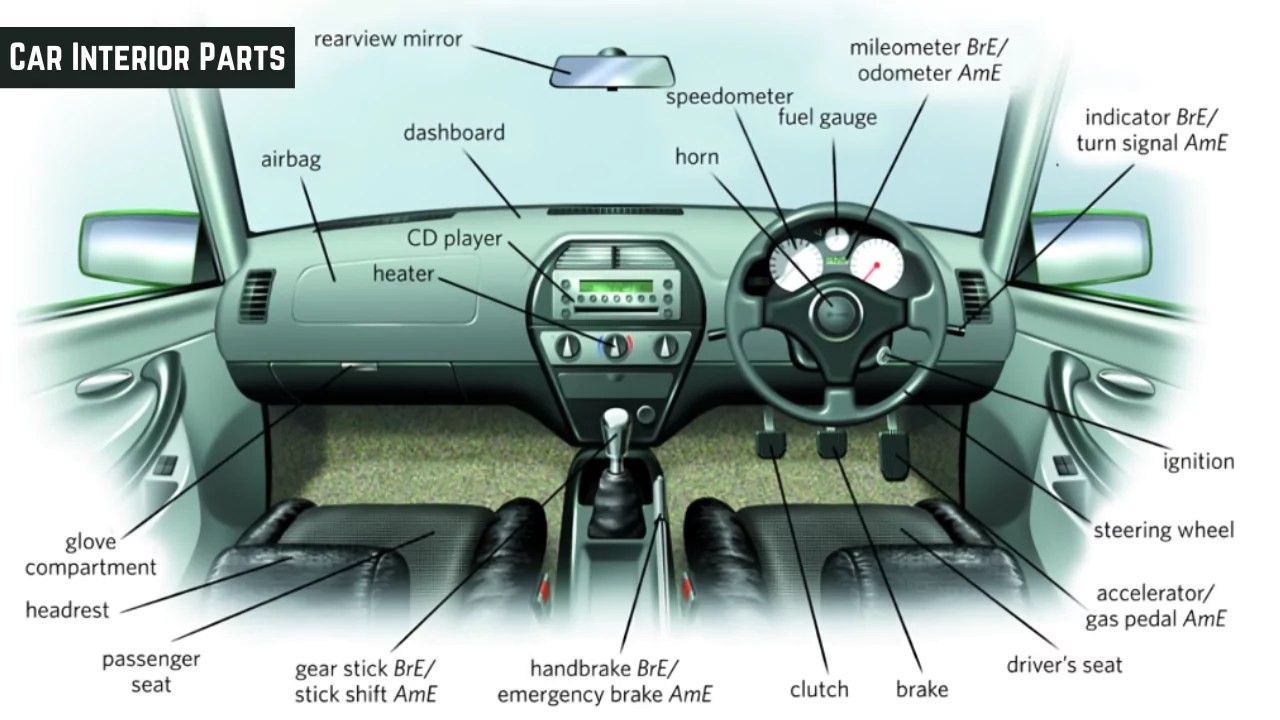
Essential Interior Parts of Automatic Cars
Here’s a breakdown of the key interior components you’ll find in most automatic cars:
- Steering Wheel and Horn
- Ignition System (Start Button/Key Slot)
- Pedals (Accelerator and Brake)
- Gear Selector
- Dashboard and Instrument Cluster
- Hazard Lights Button
- Seat Belts
- Airbags
- Rearview Mirrors (Interior and Side)
- Parking Brake (Electronic or Lever)
- Turn Signal Lever
- Center Console
- Glove Compartment
- Power Window and Door Lock Controls
- Interior Door Handles
- Audio System
- Infotainment Screen
- Sun Visors
- Car Seats
- Floor Mats
- Roof and Headliner
Exploring Automatic Car Interior Components
Let’s take a closer look at each of these interior parts, focusing on aspects relevant to automatic vehicles:
#1. Steering Wheel and Horn
The steering wheel remains the primary control for vehicle direction, even in automatic cars. It translates the driver’s input into the movement of the front wheels, ensuring precise handling. Modern automatic cars often feature power steering, making maneuvering smoother and easier, especially at low speeds.
Beyond steering, the wheel often integrates controls for various car functions. In automatic cars, you’ll frequently find buttons for cruise control (enhancing comfort on long drives), audio system adjustments, and sometimes even controls for infotainment and driver-assistance systems right on the steering wheel. This ergonomic design allows drivers to manage these features without taking their hands off the wheel, promoting safer driving in automatic vehicles.
The horn, a critical safety feature, is universally located on the steering wheel. It serves as an audible warning signal to other road users, essential for preventing accidents and alerting pedestrians.
 Steering wheel and car horn for automatic car
Steering wheel and car horn for automatic car
#2. Ignition System (Start Button/Key Slot)
In automatic cars, the ignition system can take two primary forms: a traditional key slot or a modern push-button start. Regardless of the method, this system is the gateway to powering up your vehicle.
With a key slot, you insert and turn the key to initiate the engine start sequence. Push-button start systems, increasingly common in newer automatic cars, offer keyless convenience. As long as the car detects the key fob nearby, pressing the “Start” button engages the ignition and starts the engine. Automatic cars with push-button start often include safety interlocks, requiring the brake pedal to be pressed before the engine can be started, preventing accidental starts.
The ignition system in automatic cars is electronically controlled, ensuring a smooth and reliable start every time.
#3. Pedals (Accelerator and Brake)
Automatic cars simplify driving by eliminating the clutch pedal. You’re left with two essential pedals: the accelerator (gas pedal) and the brake pedal.
The accelerator, typically the rightmost pedal, controls the engine’s throttle. Pressing it increases engine power and speed. In automatic transmissions, the car seamlessly shifts gears as you accelerate, providing smooth and effortless driving.
The brake pedal, usually larger and located to the left of the accelerator, is responsible for slowing down and stopping the vehicle. Automatic cars often feature advanced braking systems like Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Electronic Brakeforce Distribution (EBD), enhancing safety and control during braking.
#4. Gear Selector
The gear selector is a defining feature of automatic car interiors. It replaces the traditional gear stick found in manual cars, offering a simplified way to choose driving modes. Common modes in automatic cars include:
- P (Park): Locks the transmission and prevents the car from rolling. Always engage Park when stationary and turning off the engine.
- R (Reverse): Engages reverse gear for backing up.
- N (Neutral): Disengages the transmission, allowing the car to roll freely. Useful for towing short distances or in specific emergency situations.
- D (Drive): The primary mode for normal driving. The automatic transmission selects the appropriate gears based on speed and engine load.
- L (Low) or S (Sport): Some automatic cars offer a Low or Sport mode. Low gear provides more engine braking and power at lower speeds, useful for steep inclines or towing. Sport mode often changes the gear shifting points for more responsive acceleration and a sportier driving feel.
Gear selectors in automatic cars can be located on the center console, on the steering column, or even as buttons or dials in modern designs. They are designed for intuitive operation, making driving an automatic car user-friendly for drivers of all experience levels.
#5. Dashboard and Instrument Cluster
The dashboard is the command center of your car’s interior, housing vital information and controls. In automatic cars, the dashboard often incorporates features related to the automatic transmission and driving modes.
The instrument cluster, part of the dashboard, displays essential driving information. Common gauges include:
- Speedometer: Shows the vehicle’s current speed.
- Tachometer: Indicates engine revolutions per minute (RPM). While less critical in automatics, it can still provide insights into engine performance.
- Fuel Gauge: Displays the fuel level.
- Temperature Gauge: Monitors engine temperature.
- Gear Indicator: In automatic cars, this often displays the currently selected gear (P, R, N, D, etc.).
- Warning Lights: Alert the driver to potential issues with various vehicle systems, including the engine, brakes, and transmission.
Modern automatic cars are increasingly adopting digital instrument clusters, offering customizable displays and integrating features like navigation, driver-assistance information, and entertainment details.
#6. Hazard Lights Button
The hazard lights button, universally symbolized by a red triangle, activates all four turn signals simultaneously. This is a crucial safety feature for automatic and manual cars alike, used to warn other drivers of emergencies, breakdowns, or when parked in hazardous locations.
#7. Seat Belts
Seat belts are paramount safety devices in all cars, including automatics. They are designed to restrain occupants in the event of a collision, significantly reducing the risk of serious injury or fatality. Always ensure all occupants are wearing seat belts correctly before driving.
#8. Airbags
Airbags work in conjunction with seat belts to provide maximum occupant protection in crashes. Sensors in automatic cars (and all modern vehicles) detect collisions, and if the impact is severe enough, airbags deploy rapidly to cushion occupants and prevent them from hitting the hard interior surfaces of the car. Automatic cars typically feature front airbags for the driver and front passenger, and often side and curtain airbags for enhanced protection.
#9. Rearview Mirrors (Interior and Side)
Rearview mirrors are essential for driver awareness and safety. Automatic cars, like all vehicles, are equipped with an interior rearview mirror and side mirrors (driver and passenger side). These mirrors provide visibility of the road and surrounding traffic behind and to the sides of the vehicle, crucial for lane changes, turns, and parking maneuvers.
#10. Parking Brake (Electronic or Lever)
The parking brake, also known as the emergency brake, prevents the car from rolling when parked. In automatic cars, parking brakes can be either traditional lever-operated or modern electronic parking brakes. Electronic parking brakes are becoming increasingly common in automatic cars, offering push-button or switch activation and often integrating with automatic hold functions for added convenience in stop-and-go traffic.
#11. Turn Signal Lever
The turn signal lever, typically located on the left side of the steering column, activates the turn signals (indicators). Signaling your intentions to turn or change lanes is vital for safe driving in automatic and manual cars.
#12. Center Console
The center console is the area between the driver and front passenger seats. In automatic cars, the center console often houses the gear selector, cupholders, storage compartments, and controls for various vehicle functions. Modern center consoles are designed to be ergonomic and user-friendly, often incorporating infotainment system controls, climate control adjustments, and charging ports for devices.
#13. Glove Compartment
The glove compartment, located in the dashboard on the passenger side, provides a storage space for documents, small items, and the vehicle owner’s manual.
#14. Power Window and Door Lock Controls
Power window and door lock controls are standard in most modern automatic cars. These switches, usually located on the driver’s and passenger’s door panels, allow for easy operation of windows and locking/unlocking all doors simultaneously.
#15. Interior Door Handles
Interior door handles allow occupants to open the car doors from the inside. They are designed for easy and reliable operation.
#16. Audio System
The car audio system provides entertainment during drives. Automatic cars come equipped with varying levels of audio systems, from basic radios to premium sound systems with multiple speakers, amplifiers, and advanced features like smartphone integration (Apple CarPlay, Android Auto).
#17. Infotainment Screen
The infotainment screen is a central hub for information and entertainment in modern automatic car interiors. It often integrates navigation, audio controls, smartphone integration, vehicle settings, and sometimes climate control and other vehicle functions. Touchscreen interfaces are common, offering intuitive control.
#18. Sun Visors
Sun visors, located above the windshield, are adjustable flaps that block sunlight glare from the driver and front passenger’s eyes, enhancing visibility and driving comfort.
#19. Car Seats
Car seats are designed for comfort and support during driving. Automatic cars offer a wide range of seat types and materials, from basic cloth seats to premium leather upholstery. Many automatic cars feature adjustable seats, including seat height, recline, and lumbar support, for personalized comfort. Heated and ventilated seats are also common in higher trim levels.
#20. Floor Mats
Floor mats protect the car’s flooring from dirt, debris, and spills. They are easily removable for cleaning.
#21. Roof and Headliner
The roof and headliner form the interior ceiling of the car. The roof provides structural integrity, while the headliner is the fabric covering the interior roof, providing insulation, sound absorption, and a finished aesthetic to the cabin.
FAQs about Automatic Car Interior Parts
What are the main interior parts of an automatic car?
The main interior parts of an automatic car are: Steering Wheel and Horn, Ignition System, Pedals (Accelerator and Brake), Gear Selector, Dashboard, Hazard Lights Button, Seat Belts, Airbags, Rearview Mirrors, Parking Brake, Turn Signal Lever, Center Console, Glove Compartment, Power Window and Door Lock Controls, Interior Door Handles, Audio System, Infotainment Screen, Sun Visors, Car Seats, Floor Mats, Roof and Headliner.
What is the difference in interior between automatic and manual cars?
The primary interior difference between automatic and manual cars is the gear control. Automatic cars have a gear selector (like PRNDL) instead of a manual gear stick and clutch pedal. This simplifies driving and often leads to center console designs optimized for automatic gear selection and related features. However, many other interior parts are common to both types of vehicles.
Are automatic car interior parts more technologically advanced?
Automatic cars often feature more technologically advanced interiors, especially in newer models. This can include more sophisticated infotainment systems, digital instrument clusters, electronic parking brakes, and driver-assistance features integrated into the interior controls and displays. This trend is often associated with the convenience and ease-of-use focus of automatic transmissions.
How to maintain automatic car interior parts?
Maintaining automatic car interior parts is similar to maintaining any car interior. Regular cleaning, vacuuming, and using appropriate cleaning products for different materials (leather, fabric, plastic) are essential. Protecting surfaces from sun damage and promptly addressing spills will help keep your automatic car interior in good condition. For electronic components like infotainment screens, use gentle cleaning methods recommended by the manufacturer.