Just as understanding the exterior of your vehicle is crucial, knowing the Inside Car Parts Names and their functions is equally important for every car owner. Whether you are a seasoned driver or a new car enthusiast, familiarizing yourself with the components within your car’s cabin can enhance your driving experience, improve safety, and empower you to make informed decisions about maintenance and upgrades. This guide will take you through the essential inside car parts names, explaining their roles and significance.
Essential Interior Car Parts and Their Functions
The interior of a car is a complex system designed for driver and passenger comfort, control, and safety. Let’s explore the names and functions of the key components you’ll find inside your vehicle.
#1. Steering Wheel and Car Horn
The steering wheel is arguably the most fundamental control inside your car. It directly controls the direction of the vehicle by translating the driver’s rotational movements into the swiveling of the front wheels. This intricate system involves various joints and hydraulic mechanisms to ensure smooth and responsive steering.
Modern steering wheels often integrate additional functionalities such as cruise control, audio system controls, and even heating elements for added comfort. Many car owners also opt for aftermarket steering wheel covers to personalize the look and feel of their steering wheel, enhancing grip and comfort.
The car horn, typically activated by pressing the center of the steering wheel, is a vital safety feature. It allows drivers to alert other road users to their presence, warn of potential hazards, or communicate in various driving situations.
#2. Ignition
The ignition system is the starting point of your car’s journey. Usually located on the steering column or dashboard, it’s where you insert your car key or press a start button to bring the engine to life. Activating the ignition switch initiates the power supply to the engine and other essential vehicle systems, preparing your car for operation.
#3. Pedals
Looking down at the driver’s footwell, you’ll find the pedals, crucial for controlling the car’s speed and braking. In most cars, the pedal on the right is the gas pedal (accelerator), regulating the fuel supply to the engine and thus controlling the vehicle’s speed.
To the left of the gas pedal is the brake pedal. Applying pressure to the brake pedal activates the braking system, slowing down the vehicle and bringing it to a complete stop when necessary.
In vehicles with a manual transmission, you’ll find a third pedal to the left of the brake – the clutch pedal. The clutch is essential for manual gear changes, allowing the driver to disengage the engine from the transmission to smoothly shift gears and control power delivery. Automatic cars do not have a clutch pedal, as gear changes are handled automatically.
#4. Gear Shifter
The gear shifter, located in the center console between the driver and passenger seats, is used to select gears in a manual transmission vehicle. It features a shift knob indicating the gear pattern.
In automatic transmission vehicles, the equivalent is called a gear selector, often referred to as the “PRNDL” (Park, Reverse, Neutral, Drive, Low). This selector allows the driver to choose different driving modes and engage gears without manually operating a clutch.
Operating a manual gear shifter requires coordination with the clutch pedal. Depressing the clutch pedal disengages the engine, allowing the driver to move the gear shifter to the desired gear. This intricate mechanical process involves synchronizer sleeves, stop rings, and gear clutch teeth to ensure smooth and efficient gear changes.
#5. Dashboard
The dashboard is a prominent feature of the car interior, situated at the front of the cabin. It serves as a central panel housing essential gauges, indicators, and controls, while also acting as a visual divider between the front of the car and the occupants.
Dashboard designs vary significantly across car models and brands, reflecting different styles and feature sets. A typical dashboard includes several key instrument panels:
- Fuel Gauge: Displays the amount of fuel remaining in the tank, allowing drivers to monitor fuel levels and plan refueling stops.
- Speedometer: Indicates the vehicle’s current speed, helping drivers maintain safe and legal speeds.
- Tachometer: Shows the engine’s revolutions per minute (RPM), crucial for monitoring engine performance and assisting with gear shifting in manual vehicles.
- Temperature Gauge: Displays the engine’s operating temperature, warning drivers of potential overheating issues.
Modern dashboards also incorporate various warning lights and indicator lights to alert drivers to potential problems or malfunctions within the vehicle’s systems. Understanding these dashboard symbols is crucial for timely maintenance and safety.
#6. Emergency Flashers
Emergency flashers, also known as hazard lights, are activated by a dedicated button, usually marked with a triangle symbol. When engaged, all four turn signal lights flash simultaneously.
Emergency flashers are used to warn other drivers of emergency situations, such as breakdowns, accidents, or when a vehicle is parked in a hazardous location. They are a critical safety feature for alerting others to potential dangers.
#7. Car Seat Belts
Seat belts are fundamental safety devices designed to restrain occupants in the event of a collision. When worn correctly, seat belts significantly reduce the risk of serious injury or ejection from the vehicle during a crash.
Seat belts work by distributing crash forces across the stronger parts of the body, such as the chest and pelvis, and preventing occupants from colliding with the interior of the vehicle or being thrown out. Proper seat belt use is essential for the safety of all vehicle occupants.
#8. Airbags
Airbags are supplemental safety restraints designed to work in conjunction with seat belts. Located in various parts of the car interior, such as the steering wheel, dashboard, and seats, airbags inflate rapidly in the event of a significant collision.
Sensors detect the severity of a crash, and if the impact is substantial, the airbags are deployed within milliseconds, creating a cushion to protect occupants from hitting hard surfaces inside the car. Airbags are designed for one-time use and must be replaced after deployment by a qualified technician using genuine OEM replacement parts to ensure proper functionality and safety. Counterfeit airbags can be dangerous and should be avoided.
#9. Rearview Mirrors
Rearview mirrors are essential for driver visibility, providing a view of the road, vehicles, and objects behind the car. Vehicles are typically equipped with three rearview mirrors: an interior rearview mirror and two exterior rearview mirrors (driver’s side and passenger’s side).
The interior rearview mirror is mounted centrally, usually on the windshield or dashboard. It is a flat mirror, providing a unit magnification view, meaning objects appear at their actual size and distance. Exterior rearview mirrors are designed to provide a wider field of view, often using convex surfaces to enhance visibility.
#10. Emergency Brake
The emergency brake, also known as the parking brake, is an independent braking system designed to hold the vehicle stationary when parked. It operates separately from the primary hydraulic braking system.
While primarily intended for parking, the emergency brake can also be used as a backup braking system in the event of primary brake failure. It’s crucial to engage the emergency brake every time you park, regardless of the terrain or vehicle type, to prevent unintended vehicle movement. In emergency braking situations, the emergency brake can be applied gradually to help slow down or stop the vehicle if the primary brakes fail.
#11. Car Signal Lever
The car signal lever, or turn signal lever, is located on the steering column and is used to activate the turn signals (indicators). Moving the lever up or down activates the right or left turn signals respectively, indicating the driver’s intention to turn or change lanes.
The signal lever is a critical communication tool for drivers, informing other road users of intended maneuvers and promoting safe driving practices.
#12. Center Console
The center console is the area in the middle of the front cabin, between the driver and front passenger seats. In modern cars, it typically sits behind the gear shifter and often incorporates storage compartments, cupholders, and various controls.
The center console area is often built around the transmission tunnel and may extend up to the central part of the dashboard. Depending on the vehicle, the center console can house features like audio controls, climate control systems, infotainment screens, and auxiliary power outlets.
#13. Glove Compartment
The glove compartment, also known as the glove box, is a storage compartment integrated into the dashboard on the passenger side. While originally intended for gloves, it now serves as a convenient storage space for various items.
Common items stored in the glove compartment include owner’s manuals, vehicle registration and insurance documents, maps, flashlights, and other small personal items.
#14. Power Window and Door Lock Controls
Power windows and door locks are electronically operated systems that allow for convenient control of the vehicle’s windows and doors. Switches or buttons, typically located on the door panels and sometimes on the center console, allow the driver and passengers to raise and lower windows and lock or unlock doors with ease. These systems enhance convenience and security.
#15. Interior Door Handle
The interior door handle is used to open the car door from the inside. Pulling the handle disengages the door latch mechanism, allowing the door to be pushed open. Modern interior door handles are often made of plastic and are designed for ease of use and safety.
#16. Audio System
The car audio system is responsible for providing entertainment and information through sound. It comprises components such as speakers, amplifiers, and a source unit (e.g., head unit or infotainment system).
Car audio systems allow occupants to listen to music, radio, podcasts, and other audio content, enhancing the driving experience. Modern systems often integrate with smartphone connectivity, navigation, and other multimedia features.
#17. Car Central Control Screen
The car central control screen, also known as the infotainment system or multimedia display, is a central hub for various vehicle functions and information in modern cars. It combines “information” and “entertainment” into a single integrated system.
Infotainment systems can control a wide range of features, including audio, navigation, climate control, vehicle settings, smartphone integration, and more. They often utilize touchscreen interfaces, voice commands, and physical buttons for user interaction, providing a centralized and interactive control center for the vehicle.
#18. Sun Visor
Sun visors are located above the windshield, on the interior roof of the car. They are hinged flaps that can be folded down to block sunlight and reduce glare, improving visibility for the driver and front passenger, especially during sunrise or sunset.
#19. Car Seats
Car seats are designed for occupant comfort, support, and safety. They typically feature a strong frame, padding, and upholstery. Modern car seats often offer adjustable features such as seat height, backrest angle, and lumbar support to personalize comfort for different occupants.
Regular car seat maintenance, such as vacuuming and conditioning (for leather or fabric upholstery), helps to maintain their appearance and longevity. Car seat covers are a popular accessory to protect seats from wear and tear and simplify cleaning.
#20. Floor Mats
Floor mats are designed to protect the car’s interior carpeting from dirt, moisture, and wear. They are typically removable for easy cleaning and are available in various materials, such as carpet, rubber, and all-weather materials.
Floor mats play a crucial role in maintaining the cleanliness and appearance of the car’s interior. Some mats have fixation points to secure them in place.
#21. Roof and Headliner
The car roof provides structural integrity and protection to the vehicle. It offers rigidity, distributes forces in case of a rollover, and protects occupants from the elements.
The headliner is the interior fabric lining of the roof. It provides insulation against heat and noise, contributes to the interior aesthetics, and often conceals wiring and components. The roof and headliner together create a comfortable and functional cabin environment.
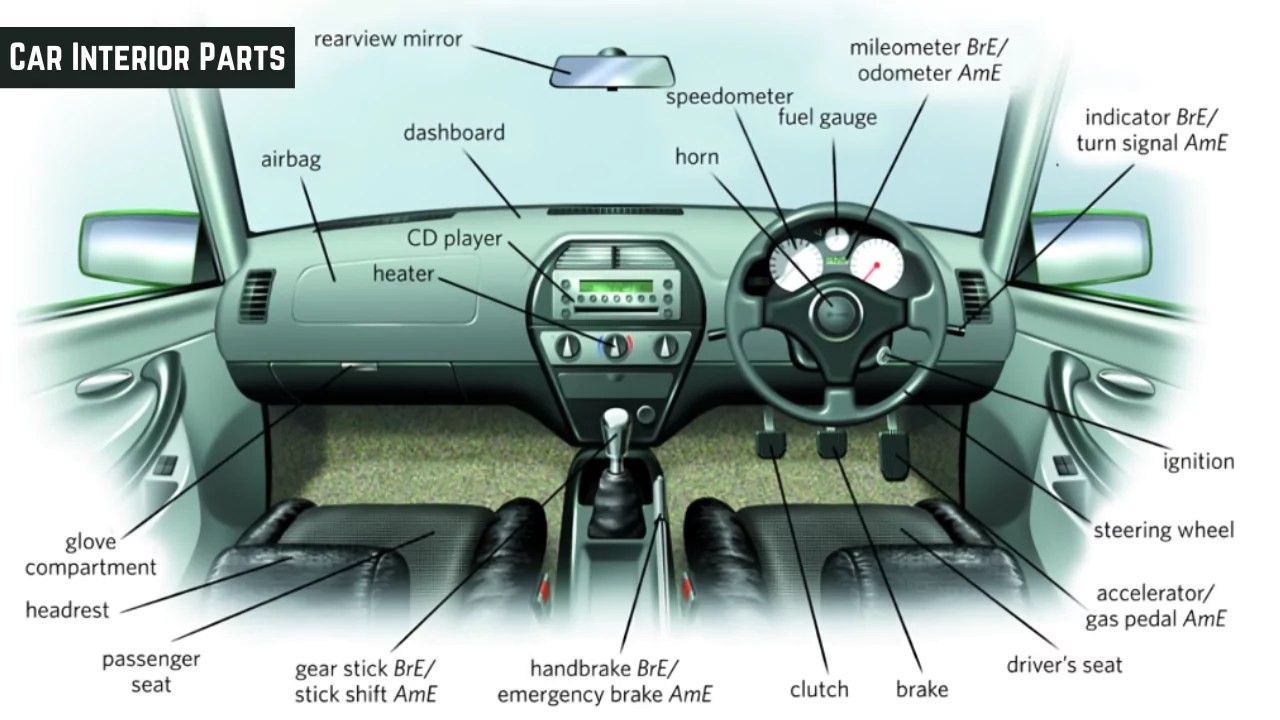 Diagram of interior car parts names
Diagram of interior car parts names
Interior Car Parts Diagram
To better visualize the location of these inside car parts, refer to the diagram above. This illustration provides a clear overview of where each component is situated within the car’s interior.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the interior parts of a car called?
The main interior parts of a car include: Steering Wheel and Car Horn, Ignition, Pedals, Gear Shifter, Dashboard, Emergency Flashers, Car Seat Belts, and Airbags, among others listed in this guide.
What is an interior panel in a car?
Interior car panels serve as coverings for the inside of the car doors and other interior surfaces. They protect internal components like window mechanisms and wiring while also contributing to the interior aesthetics.
What is the top inside of a car called?
The top inside of a car is called the headliner. It’s the fabric or material that covers the ceiling of the vehicle, providing insulation, noise reduction, and concealing structural elements and wiring.
What is a dashboard in a car?
The dashboard is a panel located at the front of the car interior, housing instruments, controls, and displays. It serves as the central interface for the driver to monitor and control various vehicle functions.
What is the interior of a car?
The interior of a car refers to the cabin space designed for occupants. It includes all the components within the vehicle’s passenger compartment, such as seats, dashboard, controls, and trim.
What are the different types of car interiors?
Car interiors can be categorized by the type of upholstery material used, including: Nylon Upholstery, Polyester Upholstery (both fabric types), Vinyl Upholstery, and Leather Upholstery, each offering different characteristics in terms of durability, comfort, and aesthetics.
Understanding the inside car parts names and their functions not only enhances your knowledge about your vehicle but also empowers you to communicate effectively with mechanics, make informed decisions about car maintenance and upgrades, and ultimately enjoy a safer and more comfortable driving experience.

