Just like the human heart, the engine is the powerhouse of your vehicle. It’s responsible for converting fuel into the energy that moves your car. This process, known as internal combustion, involves a series of precisely timed mini-explosions within the engine to generate power. While often thought of as a single unit, the engine is a complex assembly of numerous interconnected components. Understanding the Car Engine All Parts Name and their functions is crucial for every car owner. This knowledge not only empowers you with a better understanding of your vehicle but also aids in recognizing potential issues and communicating effectively with mechanics.
 Detailed view of a car engine's internal components and layout
Detailed view of a car engine's internal components and layout
Essential Car Engine Parts and Their Functions
Modern car engines are built around robust, sealed metal cylinders. Most cars today feature engines with four to eight cylinders, although some high-performance vehicles can have up to twelve or even sixteen. These cylinders operate in a synchronized manner, opening and closing at precise moments to allow fuel intake, combustion, and exhaust gas expulsion. Let’s delve into some of the most vital car engine all parts name and explore their roles:
Engine Block: The Foundation
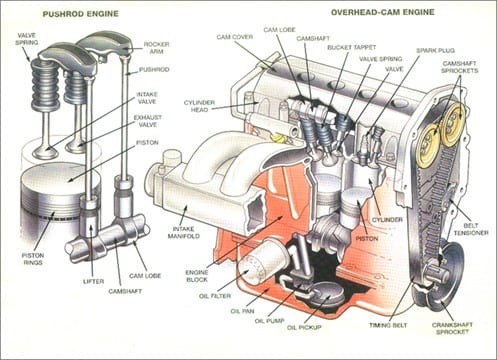
The engine block is the core structure of the engine, often constructed from aluminum or cast iron. It’s engineered with multiple cylindrical bores that house the cylinders and intricate channels for coolant and oil circulation. These pathways are essential for engine cooling and lubrication. The engine block provides the structural support for key components like the pistons, crankshaft, and camshaft. Depending on the vehicle, cylinder arrangements within the block can be inline, flat, or V-shaped.
Pistons: Converting Combustion into Motion
Pistons are cylindrical components with a flat top that move vertically inside the cylinders. Their primary function is to receive the force generated by combustion and transmit it to the crankshaft, ultimately propelling the vehicle. Each piston moves up and down twice for every crankshaft rotation. In an engine running at 1250 RPM, pistons can travel up and down an astounding 2500 times per minute. Piston rings, located within grooves on the piston, are critical for maintaining cylinder compression and minimizing friction against the cylinder walls.
Crankshaft: Transforming Linear to Rotational Motion
Positioned in the lower section of the engine block within crankshaft journals (bearing surfaces), the crankshaft is a meticulously crafted and balanced component. Connected to the pistons via connecting rods, the crankshaft converts the pistons’ reciprocating (up and down) motion into rotary motion, which is essential for powering the drivetrain. This rotational force is then used to turn the wheels and drive the vehicle.
Camshaft: Orchestrating Valve Timing
The camshaft’s location varies based on engine design, sometimes residing in the engine block or within the cylinder heads. Modern engines often employ overhead camshafts, either Dual Overhead Camshaft (DOHC) or Single Overhead Camshaft (SOHC) configurations. Supported by oil-lubricated bearings for durability, the camshaft regulates the timing of valve opening and closing. It converts the crankshaft’s rotary motion into a vertical motion to control lifters, which in turn operate pushrods, rockers, and ultimately, the valves.
Cylinder Head: The Control Center for Air and Exhaust Flow
Attached to the engine block with cylinder head bolts and sealed with a head gasket, the cylinder head is a complex component. It houses valve springs, valves, lifters, pushrods, rockers, and camshafts. Crucially, it manages the intake and exhaust passages. During the intake stroke, it allows air to enter the cylinders, and during the exhaust stroke, it facilitates the removal of exhaust gases. The head gasket is vital for maintaining a seal between the engine block and cylinder head, preventing leaks and ensuring proper combustion.
Timing Belt/Chain: Synchronizing Engine Operations
To ensure the engine runs smoothly and efficiently, the camshaft and crankshaft must be precisely synchronized. This synchronization is achieved by either a timing belt or a timing chain. A timing belt is typically made of durable rubber with teeth that mesh with pulleys on the camshaft and crankshaft. A timing chain, similar to a bicycle chain, wraps around toothed pulleys. Both components ensure that valves open and close at the exact right moment in relation to piston movement, which is critical for proper engine function.
Common Engine Problems and Symptoms
Given the intricate nature of the engine and the high-speed operation of its parts, wear and tear are inevitable over time. This can lead to various engine problems. Recognizing the symptoms associated with these issues can help you address them promptly and prevent more significant damage. Here are some common engine problems and their telltale signs:
- Poor Compression: This can result in reduced engine power, engine misfires, or even a no-start condition.
- Cracked Engine Block: Often leads to engine overheating, visible smoke from the exhaust, and coolant leaks, frequently noticeable on the engine’s exterior.
- Damaged Pistons, Rings, and/or Cylinders: Symptoms include unusual rattling noises, blue-tinted smoke from the exhaust, rough engine idling, or failure to pass emissions tests.
- Broken or Worn Rods, Bearings, & Pins: Can manifest as tapping or ticking sounds, low engine oil pressure, metallic particles in the engine oil, or rattling sounds during acceleration.
While car engines may appear complicated, their fundamental purpose is straightforward: to propel your vehicle. The coordinated effort of numerous car engine all parts name is essential for generating this motion. Regular vehicle maintenance is paramount to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your engine components. Adhering to scheduled oil changes, coolant and fluid flushes, and replacing belts and hoses at recommended intervals are proactive steps to prevent engine failures.
For expert engine maintenance and repair, consider seeking services from certified professionals. Reliable service centers like Sun Auto Service, known for their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, can provide the necessary care to keep your engine running smoothly for years to come. Maintaining your engine properly ensures its longevity and reliability, keeping you safely on the road.