When your car needs a repair, locating the correct replacement part is the first crucial step. Whether you’re a seasoned DIY mechanic or a car owner tackling minor repairs, understanding How To Find Car Part Numbers is essential for ensuring compatibility, quality, and a smooth repair process. Navigating the world of auto parts can be confusing, especially when faced with choices between Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and aftermarket options. This guide will provide you with expert insights on how to find car part numbers efficiently and accurately, empowering you to make informed decisions for your vehicle’s maintenance.
What are OEM Car Parts?
OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer. These are parts manufactured either directly by your car’s maker or by a company authorized by them, built to the exact specifications and standards used when your car was originally assembled. Choosing OEM car parts offers peace of mind, as they are designed to perfectly fit your vehicle and maintain its original performance and safety standards.
OEM parts come with several advantages. Firstly, they guarantee compatibility. Being made to the manufacturer’s precise requirements, they eliminate guesswork and ensure seamless integration with your car’s existing systems. Secondly, OEM parts often come with a warranty, protecting you against defects and ensuring quality. This warranty can be particularly valuable for critical components, offering reassurance and financial protection.
It’s important to distinguish OEM from “genuine” parts. While often used interchangeably, genuine parts are specifically those that carry the car manufacturer’s logo and are packaged in their branded boxes. They are produced in-house by the car manufacturer themselves. OEM parts, on the other hand, might be made by a third-party supplier but still adhere to the car manufacturer’s stringent specifications. In terms of quality and fit, OEM and genuine parts are virtually identical, both representing the highest standard available for your vehicle.
What are Aftermarket Car Parts?
Aftermarket car parts are manufactured by third-party companies that are not directly affiliated with your car’s original manufacturer. These parts are designed to be compatible with a range of vehicle makes and models and offer an alternative to OEM components. Often referred to as “non-OEM” or “generic” parts, aftermarket options can present both advantages and disadvantages.
The primary appeal of aftermarket parts is often their lower price point compared to OEM parts. This cost saving can be significant and make repairs more budget-friendly. However, it’s crucial to understand that the lower price may sometimes reflect differences in material quality, manufacturing processes, or design precision.
While some aftermarket parts may indeed offer comparable or even enhanced performance compared to OEM, quality can vary significantly between brands and part types. Some aftermarket manufacturers specialize in producing high-quality components that meet or exceed OEM standards. Conversely, some may prioritize cost savings over quality, potentially leading to reduced lifespan or performance issues.
When considering aftermarket parts, it’s vital to research reputable brands and read reviews to gauge the quality and reliability of the specific part. Factors like warranty, materials used, and manufacturing certifications can provide insights into the part’s expected performance and longevity. While aftermarket parts can be a cost-effective solution, careful evaluation is necessary to ensure you’re not compromising on safety or long-term reliability.
Why Finding the Correct Part Number is Crucial
Locating the correct car part number is not just about convenience; it’s about ensuring the safety, performance, and longevity of your vehicle. Using the precise part number guarantees you are getting the exact component designed for your car’s make, model, and year. This precision is paramount for several reasons:
Firstly, perfect fit: OEM part numbers, and even reliable aftermarket part numbers, ensure the replacement component will fit seamlessly into your vehicle. Incorrect parts can lead to installation difficulties, damage to surrounding components, or even functional failure of the system.
Secondly, performance and compatibility: Car parts are designed to work in conjunction with other systems in your vehicle. Using the correct part number ensures that the replacement will perform as intended and maintain the overall efficiency and performance of your car. Mismatched parts can lead to reduced performance, system malfunctions, and potential safety hazards.
Thirdly, avoiding costly mistakes: Ordering the wrong part can lead to wasted time, money, and effort. Incorrect parts may need to be returned, incurring restocking fees and delays in your repair. Furthermore, attempting to fit an incompatible part could potentially damage your vehicle, leading to more extensive and expensive repairs down the line.
By taking the time to accurately find your car part number, you are investing in a smoother, more effective repair process, minimizing risks and ensuring your vehicle operates safely and reliably.
Methods to Find Car Part Numbers
There are several reliable methods to find car part numbers, each suited to different situations and levels of accessibility. Here are the most effective approaches:
1. Check the Part Itself
Your first and often most direct approach to finding a car part number is to examine the component that needs replacing. Most car parts, especially OEM components, will have the part number directly printed or engraved on them. This number is usually located on a sticker, a quality control plate, or stamped directly into the part itself.
When examining the part, look for alphanumeric codes that may include letters, numbers, and sometimes dashes. Unfortunately, there isn’t a universal format for OEM part numbers across all manufacturers. Each car brand has its own system, making it essential to carefully transcribe the entire code you find.
For example, Volvo part numbers tend to be straightforward, often consisting of numbers only without dashes, like 30640811 for a rotor screw in certain models. In contrast, Mazda part numbers frequently incorporate letters and numbers, separated by dashes, such as KD33-43-55 YD for a reservoir cap.
(The URL is used as requested, but ideally, a different image showing examples of part numbers on actual car parts would be more relevant here. If only one image is allowed and this is the most suitable from the original article, we will keep it and adjust the alt text accordingly to be more generic about finding information on car parts.)
Alt text: Diagram illustrating how to locate vehicle information which can be used to find car part numbers, relevant to the topic of finding car parts.
While locating the part number directly on the component is often the quickest method, it’s not always feasible. The old part might be damaged beyond recognition, the number might be faded or illegible due to wear and tear, or you might not have the old part available if it was lost or completely disintegrated. In these cases, alternative methods are necessary.
2. Contact the Car Manufacturer or Dealership
When you cannot retrieve the part number from the component itself, contacting your car’s manufacturer or a local dealership is a highly reliable alternative. Dealerships have access to comprehensive parts databases linked to your vehicle’s specific make, model, and year.
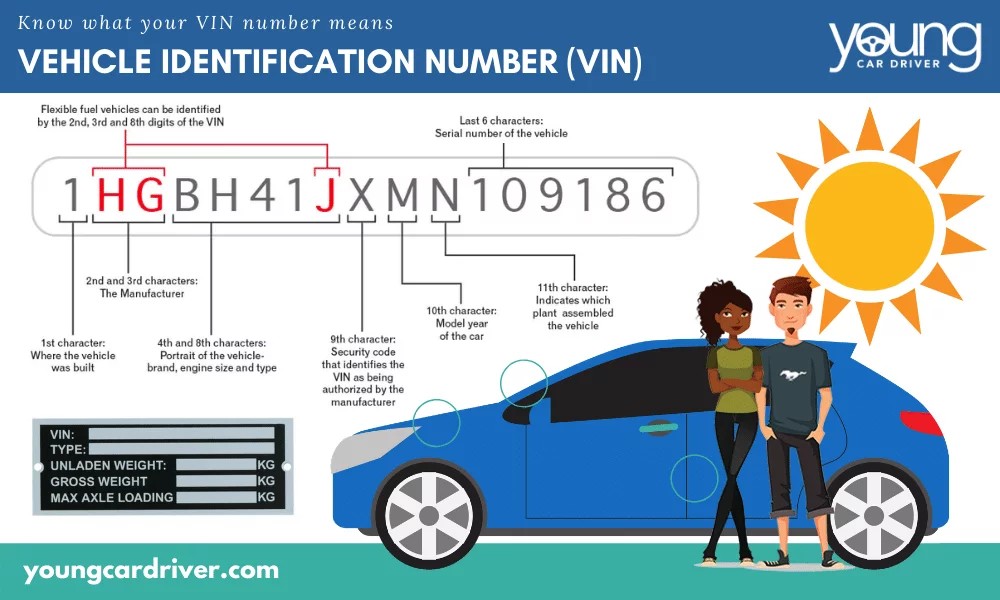
To effectively utilize this method, you will need to provide the dealership with accurate information about your car. The most crucial piece of information is your Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). The VIN is a unique 17-digit code assigned to your car, acting like its fingerprint. It contains detailed information about your car’s manufacturing specifications, including the exact parts originally installed.
Along with the VIN, be prepared to provide details about the specific part you need. Describing the part’s function, location in the car, and any visual characteristics will help the dealership parts department accurately identify the component and its corresponding part number. Dealerships have trained parts specialists who can use this information, along with the VIN, to pinpoint the correct OEM part number for your vehicle.
3. Use Your Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
Leveraging your car’s Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is a powerful and versatile method for finding car part numbers. As mentioned earlier, the VIN is a unique identifier that holds a wealth of information about your specific vehicle. It acts as a key to unlock detailed parts information tailored to your car’s exact specifications.
Locating your VIN is usually straightforward. The most common location is on the dashboard, visible from outside the car on the driver’s side, where the dashboard meets the windshield. You can also find the VIN on your car’s registration documents, insurance paperwork, and often on a sticker inside the driver’s side doorjamb.
Alt text: VIN diagram explaining the structure and information contained within each section of a Vehicle Identification Number, useful for identifying car parts.
Once you have your VIN, you can use it in several ways to find part numbers:
- Online VIN Decoders: Numerous online VIN decoder websites allow you to input your VIN and retrieve detailed information about your car, including potential part numbers. Some specialized parts websites also integrate VIN decoders directly into their part search tools.
- Parts Websites and Online Retailers: Many online auto parts retailers allow you to search for parts by VIN. By entering your VIN, the website filters results to show only parts compatible with your specific vehicle, streamlining the search process and increasing accuracy.
- Local Auto Parts Stores: Even brick-and-mortar auto parts stores can utilize your VIN to look up compatible parts in their systems. Providing your VIN to the parts specialist at the counter can significantly expedite the process of finding the correct components.
Besides the dashboard, VINs can also be found in these locations on your car:
- Driver’s side front door frame column: On a sticker when you open the driver’s door.
- Machined pad on the front of the engine: Less common but sometimes engraved on the engine block.
- Inside the left side wheel arch: Stamped on the chassis in the wheel well.
- Steering wheel or steering column: Engraved on the steering column itself.
- Radiator support bracket: Stamped on the metal bracket supporting the radiator.
By utilizing your VIN, you can confidently narrow down your search for car parts and ensure compatibility, whether you are searching online, at a dealership, or at your local auto parts store.
OEM vs. Aftermarket Parts: A Detailed Comparison
Choosing between OEM and aftermarket parts involves weighing several factors to determine the best option for your needs and budget. Both OEM and aftermarket parts have their own sets of pros and cons:
OEM Parts:
Pros:
- Guaranteed Fit: Designed to the exact specifications of your vehicle, ensuring perfect fit and compatibility.
- Assured Quality: Meet the manufacturer’s standards for quality and performance, often providing reliability and longevity.
- Warranty Coverage: Often covered by the manufacturer’s warranty, offering protection against defects.
- Maintains Vehicle Value: Using OEM parts can help maintain your car’s original condition and potentially its resale value.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: Typically more expensive than aftermarket parts due to branding, stricter manufacturing processes, and warranty provisions.
- Limited Availability: May sometimes be available only through dealerships or specific OEM parts suppliers.
Aftermarket Parts:
Pros:
- Lower Price: Generally more affordable than OEM parts, offering cost savings on repairs.
- Wider Availability: Readily available from numerous retailers, online stores, and auto parts shops.
- Variety of Brands and Options: Extensive selection of brands, quality levels, and feature options to choose from.
- Potential Performance Upgrades: Some aftermarket parts are designed to improve upon OEM performance in specific areas.
Cons:
- Variable Quality: Quality can vary significantly between brands and parts; careful research is needed.
- Potential Fitment Issues: While many aftermarket parts are designed for broad compatibility, fitment can sometimes be less precise than OEM.
- Limited or No Warranty: Warranty coverage can be less comprehensive or shorter than OEM warranties, depending on the brand.
- Potential Impact on Vehicle Value: Using non-OEM parts might, in some cases, slightly affect perceived vehicle value.
Making the Choice:
The decision between OEM and aftermarket parts depends on your priorities. If you prioritize guaranteed fit, assured quality, and warranty coverage, and budget is less of a concern, OEM parts are a solid choice. If you are looking for cost savings, have researched reputable aftermarket brands, and are comfortable with potentially slightly variable quality, aftermarket parts can be a viable alternative. For critical components related to safety or essential vehicle systems, many experts recommend OEM parts for maximum reliability. For less critical components or cosmetic parts, reputable aftermarket brands can offer a good balance of cost and quality.
Conclusion
Finding the correct car part number is a crucial step in any vehicle repair or maintenance endeavor. By understanding the methods outlined in this guide – checking the part itself, contacting the manufacturer, and utilizing your VIN – you can confidently locate the precise components you need. Whether you opt for OEM parts for guaranteed quality and fit, or explore reputable aftermarket options for budget-conscious repairs, having the correct part number empowers you to make informed decisions and ensure your vehicle’s continued performance and reliability.
If your car repairs are becoming frequent and costly, it might be time to consider whether ongoing maintenance is the most economical solution. If you’re facing significant repair bills, exploring options such as selling your car for scrap or salvage could be a practical alternative. Consider evaluating the overall condition of your vehicle and the cumulative cost of repairs versus the value of your car. This assessment can help you determine the most financially sensible path forward for your automotive needs.