Just like the human body has organs to perform various functions, a car machine relies on numerous parts working in harmony, with the engine at its heart. The primary role of your car’s engine is to convert fuel into motion. This is achieved through a process of internal combustion, essentially controlled mini-explosions that generate power. While often perceived as a single unit, the engine is actually a complex assembly of individual components, each playing a vital role. Understanding the names and functions of these car machine parts is crucial for any car owner. Let’s delve into the essential components that make your vehicle move.
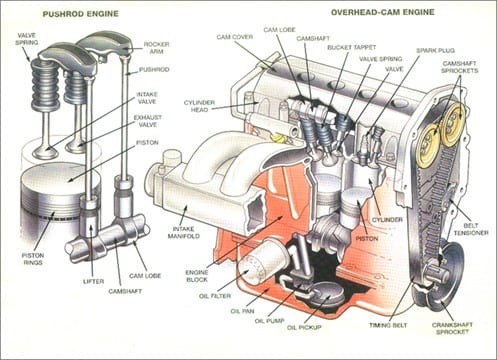 Car engine diagram
Car engine diagram
Car engines are built around robust metal cylinders, designed to be sealed and resilient. Modern cars typically house between four and eight cylinders, although high-performance vehicles can have as many as sixteen. These cylinders operate with precise timing, orchestrating the intake of fuel for combustion and the expulsion of exhaust gases. Among the many parts of a car machine engine, some are more critical than others. Here’s a breakdown of the most essential car engine parts and their functions, as shown in the diagram.
-
Engine Block: Considered the foundation of the engine, the engine block is typically constructed from aluminum or iron. It’s engineered with multiple cylindrical bores to house the cylinders and incorporates passages for coolant and oil circulation, essential for engine temperature regulation and lubrication. Oil pathways are designed to be narrower than coolant passages. The engine block is also the primary housing for key components such as pistons, the crankshaft, the camshaft, and, depending on the vehicle’s design, four to twelve cylinders arranged in inline, flat, or V configurations.
-
Pistons: These cylindrical components feature a flat top surface and are responsible for converting the energy from combustion into mechanical work that propels the car. Pistons move vertically within the cylinders, completing two full strokes (up and down) for each rotation of the crankshaft. In an engine operating at 1250 RPM, each piston travels up and down an astounding 2500 times every minute. Piston rings, located within grooves on the piston, are vital for maintaining cylinder compression and minimizing friction against the cylinder walls.
-
Crankshaft: Situated in the lower section of the engine block, within crankshaft journals (bearing surfaces), the crankshaft is a meticulously crafted and balanced component. It connects to the pistons via connecting rods. Functioning similarly to a jack-in-the-box mechanism, the crankshaft transforms the linear up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotary motion, operating at the engine’s speed. This rotational force is then transmitted to the transmission system, ultimately driving the wheels.
-
Camshaft: The location of the camshaft varies depending on the vehicle’s engine design. It may be positioned within the engine block or in the cylinder heads. Many contemporary vehicles utilize cylinder head placement, often featuring Dual Overhead Camshaft (DOHC) or Single Overhead Camshaft (SOHC) configurations. Camshafts are supported by a series of oil-lubricated bearings to ensure longevity and smooth operation. The camshaft’s primary function is to precisely control the timing of valve opening and closing. It converts the crankshaft’s rotary motion into an up-and-down motion, which is then used to actuate lifters, pushrods, rockers, and ultimately, the valves.
-
Cylinder Head: Secured to the engine block by cylinder bolts and sealed with a head gasket, the cylinder head is a complex component housing numerous parts. These include valve springs, valves, lifters, pushrods, rockers, and camshafts. The cylinder head manages the intake and exhaust processes, controlling passageways that allow fresh air to enter the cylinders during the intake stroke and channels for exhaust gases to exit during the exhaust stroke. Precise control over these flows is critical for efficient combustion.
-
Timing Belt/Chain: Synchronization between the camshaft and crankshaft is paramount for proper engine operation and precise combustion timing. This synchronization is achieved by either a timing belt or a timing chain. A timing belt is constructed from durable rubber reinforced with cogs that interlock with pulleys on the camshaft and crankshaft. A timing chain, similar to a bicycle chain, wraps around toothed pulleys. Both systems ensure the valves open and close in perfect coordination with piston movement, which is essential for engine efficiency and performance.
Common Issues in Car Machine Engines
Given the intricate nature of car machine engines, with numerous parts performing high-speed, complex tasks, wear and tear over time is inevitable. This can lead to various engine problems and changes in your car’s performance. Here are some common engine issues and their associated symptoms:
-
Poor Compression: This often results in reduced engine power, engine misfires, or even a no-start condition. Low compression can be caused by worn piston rings, valve issues, or cylinder head gasket leaks.
-
Cracked Engine Block: A crack in the engine block can lead to serious problems such as engine overheating, white smoke emanating from the exhaust pipe, and coolant leaks, often visible on the exterior of the engine block.
-
Damaged Pistons, Rings, or Cylinders: Symptoms of damage in these parts include rattling noises from the engine, blue-tinted smoke from the exhaust, rough idling, and failure to pass emissions tests. These issues often indicate excessive oil burning due to compromised sealing or cylinder wall damage.
-
Broken or Worn Rods, Bearings, and Pins: These problems can manifest as tapping or ticking sounds originating from within the engine, low engine oil pressure, metallic particles found in the engine oil during an oil change, or rattling sounds particularly noticeable during acceleration. These symptoms suggest serious internal engine wear requiring immediate attention.
Car machine engines, while intricate and sophisticated, serve a fundamental purpose: to propel your vehicle. The seamless operation of numerous interconnected components is essential for generating this motion. Regular and proper vehicle maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and reliability of these parts. Routine oil changes, periodic fluid flushes, and timely replacement of belts and hoses, as recommended by your vehicle manufacturer, are proactive steps to prevent major engine failures.
For specialized engine maintenance and repair services, it’s important to choose a reputable service center. Seek out a trusted provider committed to honest and high-quality workmanship. A reliable service center will offer certified technicians, transparent communication, and warranties on their services, ensuring your peace of mind and the long-term health of your car machine engine.