When your car needs a repair, finding the right replacement part is crucial. Using the wrong part can lead to further damage, safety issues, and wasted time and money. Identifying the correct part number is the first and most important step in ensuring you get the exact component your vehicle requires. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about finding the part number for your car, whether you’re dealing with routine maintenance or a more complex repair.
Understanding OEM and Aftermarket Car Parts
Before diving into how to find a part number, it’s important to understand the different types of car parts available: OEM and aftermarket. Knowing the difference can influence your part search and purchasing decisions.
What are OEM Car Parts?
OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer. OEM parts are made either by your car’s manufacturer or by a company contracted by them, and are produced to the exact specifications of the original parts used when your car was built. Choosing OEM car parts offers several advantages:
- Guaranteed Quality: OEM parts are designed to meet the high standards set by your car’s manufacturer, ensuring they are reliable and durable.
- Perfect Fit: Being made to original specifications means OEM parts are guaranteed to fit perfectly, simplifying installation and ensuring optimal performance.
- Warranty Coverage: Using OEM parts often maintains your car’s warranty, offering peace of mind in case of future issues.
While they may sometimes be manufactured by external companies, OEM parts are indistinguishable from the originals in terms of quality and specifications. They may not always carry the car manufacturer’s logo, but they are produced to the same rigorous standards.
It’s also worth distinguishing OEM parts from “genuine” parts. Genuine parts are manufactured directly by the car maker and always carry the manufacturer’s logo. Essentially, genuine parts are a subset of OEM parts, representing those specifically branded by the car manufacturer.
What are Aftermarket Car Parts?
Aftermarket car parts are produced by third-party companies that are not directly affiliated with your car’s original manufacturer. These parts are designed to be compatible with various makes and models. Aftermarket parts offer their own set of considerations:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Aftermarket parts are generally less expensive than OEM parts, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious car owners.
- Wider Availability: A vast range of aftermarket parts are available from numerous manufacturers and retailers, offering more choices and potentially easier access.
- Performance Variations: While some aftermarket parts may match or even exceed OEM quality, the quality can vary significantly. Some aftermarket parts might be designed for enhanced performance or specific driving needs.
However, there are potential downsides to consider with aftermarket parts:
- Quality Concerns: The quality of aftermarket parts can be inconsistent. Choosing reputable brands and suppliers is crucial to avoid inferior parts.
- Fitment Issues: While designed to be compatible, aftermarket parts may not always offer the perfect fit of OEM parts, potentially leading to installation challenges or compromised performance.
- Warranty Implications: Using aftermarket parts might, in some cases, affect your car’s warranty, particularly if the part is deemed to be the cause of a subsequent issue.
When choosing between OEM and aftermarket parts, consider the specific part needed, your budget, desired quality, and warranty implications. For critical components, OEM parts often provide greater assurance, while for less critical parts, reputable aftermarket options can offer significant savings.
How to Find the OEM Part Number for Your Car
Now, let’s explore the methods to find the crucial OEM part number for your car. This number is your key to sourcing the correct replacement part, whether you choose OEM or use it as a reference for finding a compatible aftermarket option.
1. Check the Part Itself
Your first and often easiest method is to examine the part itself. If you have the old part in hand, or if you can access the part in your car, look for the part number directly on the component.
- Location: Part numbers are typically stamped, etched, or printed directly onto the part. Look for stickers, plates, or markings on the part’s surface.
- Quality Control Sticker/Plate: Often, the part number is located on a quality control sticker or plate attached to the component. This is a good place to start your search.
- Number Format: Be aware that there isn’t a universal format for OEM part numbers. Each manufacturer has its own system. Part numbers are usually alphanumeric and may include dashes.
For example, as mentioned in the original article, Volvo part numbers are typically all numbers without dashes, while Mazda uses letters, numbers, and dashes. Understanding this variation is important when visually scanning a part for its number.
Even if the part number format looks unfamiliar, carefully examine any series of numbers and letters on the part. It’s likely to be the OEM part number or a key identifier that can lead you to it.
2. Contact the Car Manufacturer or Dealership
If you can’t find the part number on the part itself, or if the number is illegible due to damage or wear, contacting your car manufacturer or a dealership is a reliable alternative.
- Provide Vehicle Information: When contacting them, be ready to provide your car’s make, model, year, and VIN (Vehicle Identification Number). The VIN is particularly important as it uniquely identifies your specific vehicle and its original components.
- Describe the Part Needed: Clearly describe the part you need. Be as specific as possible, including its location in the car and its function. If possible, providing a photo can also be helpful.
- Request the OEM Part Number: Specifically ask for the OEM part number for the component you’ve described. Dealership parts departments are equipped to look up part numbers based on your vehicle’s VIN and the part description.
This method is especially useful when you don’t have the old part available, or when you need to verify the part number’s accuracy before ordering.
3. Use Your Car’s VIN Number
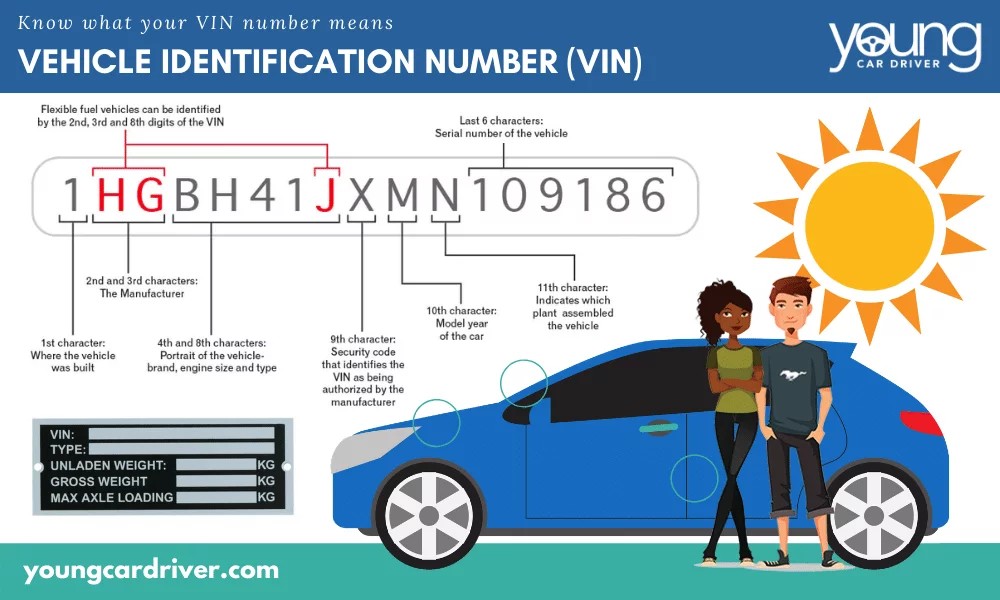
Your car’s VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) is a unique 17-digit code that acts as your car’s fingerprint. It contains detailed information about your vehicle, including its make, model, year of manufacture, assembly plant, and original equipment. The VIN is an invaluable tool for finding the correct part number.
- Locate Your VIN: The VIN is typically found in several locations:
- Dashboard: Stand outside your car on the passenger side and look at the bottom corner of the windshield where it meets the dashboard. The VIN is usually visible through the glass.
- V5C Logbook (Vehicle Registration Certificate): Your car’s registration document will prominently display the VIN.
- Driver’s Side Door Frame: Open the driver’s side door and look at the doorjamb or doorpost. There’s often a sticker or plate with the VIN.
- Other Locations: Less common locations include the engine block, inside the wheel arch, steering column, or radiator support bracket.
- Using the VIN to Find Part Numbers:
- Dealership Parts Department: As mentioned earlier, dealerships can use your VIN to precisely identify the correct OEM part numbers for your car.
- Online Parts Websites: Many online auto parts retailers and OEM parts websites have VIN lookup tools. You can enter your VIN, and the website will display parts specifically compatible with your vehicle.
- Parts Databases: Some online databases and parts catalogs allow you to search for parts based on your VIN, providing OEM part numbers and compatibility information.
Decoding Your VIN (Optional):
While you don’t need to decode your VIN to find part numbers, understanding its structure can be interesting. The VIN is composed of three sections:
- World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI): The first three characters identify the manufacturer and region of origin.
- Vehicle Descriptor Section (VDS): Characters 4-9 describe the vehicle’s attributes like body style, engine type, and model.
- Vehicle Identifier Section (VIS): Characters 10-17 are unique to your specific vehicle and include the model year, assembly plant, and serial number.
Youngcardriver.com provides a helpful diagram explaining the VIN structure, which can further enhance your understanding of your car’s unique identification.
4. Utilize Online Part Number Lookup Tools and Databases
The internet offers a wealth of resources for finding car part numbers. Online part number lookup tools and databases can streamline your search and provide quick access to the information you need.
- OEM Parts Websites: Many car manufacturers have official parts websites where you can search for parts using your VIN or by entering vehicle details. These sites typically provide exploded diagrams and detailed part information, including OEM part numbers.
- Aftermarket Parts Retailer Websites: Major aftermarket parts retailers often have online catalogs with part lookup tools. You can usually search by vehicle make, model, year, and then browse parts categories or use keywords to find the component you need. These sites may show both OEM and aftermarket part options.
- Specialized Parts Databases: Several online databases and catalogs are specifically designed for finding car parts. Some are subscription-based and used by professionals, while others offer free limited access. These databases often provide cross-referencing between OEM and aftermarket part numbers and detailed technical specifications.
When using online tools, always double-check the information and compatibility, especially when dealing with aftermarket parts. Cross-referencing information from multiple sources is a good practice to ensure accuracy.
Choosing Between OEM and Aftermarket Parts: Key Considerations
Once you have the OEM part number and understand your options, the final step is deciding whether to go with OEM or aftermarket parts. Here’s a summary of key differences to help you make an informed choice:
| Feature | OEM Parts | Aftermarket Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Generally more expensive | Generally less expensive |
| Quality | Guaranteed to meet original standards | Quality varies; reputable brands are essential |
| Fitment | Perfect fit, designed for specific vehicle | Fit may vary; some are universal or less precise |
| Warranty | Often covered under car’s warranty | Warranty depends on the aftermarket manufacturer |
| Availability | May be more limited for older models | Widely available |
| Branding | May have car manufacturer’s or OEM logo | Branded with the aftermarket company’s logo |
| Performance | Original performance | Performance can be equal to, better, or worse |

Consider your priorities: If you prioritize guaranteed quality, perfect fit, and maintaining your car’s original specifications, OEM parts are the best choice. If you are looking for cost savings and are comfortable researching reputable aftermarket brands, aftermarket parts can be a viable option.
Conclusion
Finding the correct part number for your car is the foundation of successful car repair and maintenance. By utilizing the methods outlined in this guide – checking the part itself, contacting the manufacturer, using your VIN, and leveraging online resources – you can confidently identify the parts you need. Whether you choose OEM or aftermarket parts, having the correct part number empowers you to make informed decisions, ensuring your car gets the right components for reliable and safe operation.
If you find that repairs are becoming too frequent or costly, it might be time to consider other options. Selling your car for scrap or salvage can be a practical solution. Websites like Scrap Car Comparison can help you find the best offers from scrap car buyers in your area, making the process of selling your old vehicle straightforward and efficient.