Just like the human body, a car is composed of numerous parts that work together to ensure its functionality and performance. Understanding the names of car body parts is not only essential for car enthusiasts but also for car owners who want to communicate effectively with mechanics, perform basic maintenance, or simply deepen their knowledge about their vehicles.
Have you ever wondered about the specific names of each component when looking at your vehicle’s exterior? This comprehensive guide will explore the major body parts of a car, providing you with their names and functions. Whether you’re a seasoned auto expert or a curious car owner, this article will enhance your understanding of “Car All Body Parts Name”.
Exploring the Main Car Body Parts Names
Below is a detailed list of the primary components that constitute a car’s body. This list covers everything from the outer shell to the smaller, but equally important, trim pieces.
- Body Shell: The foundational structure of the car, onto which all other body parts are attached. It’s the main frame that gives the car its shape and structural integrity, excluding doors, windows, and mechanical components.
- Hood or Bonnet: The hinged cover over the engine compartment in front-engine vehicles. It protects the engine and allows access for maintenance and repairs.
- Front Bumper: A protective bar at the front of the car designed to absorb impact during a collision, minimizing damage to the body.
- Rear Bumper: Similar to the front bumper, it protects the rear of the car from impacts.
- Bumper Grille: Located within the bumper, it allows airflow to the engine for cooling, often designed with mesh patterns and unique styles for different car models.
- Crash Guard or Bullbar: Metal bars added to the front or rear of a vehicle for extra protection against collisions, particularly useful in off-road or rural driving conditions.
- Headlight: Lamps at the front of the vehicle to illuminate the road ahead, crucial for nighttime driving and visibility.
- Fog Lamp: Lights mounted lower than headlights, designed to improve visibility in foggy or adverse weather conditions by cutting through the mist and illuminating the road closer to the ground.
- Indicator Lights (Signal Lights or Turn Signals): Flashing lights at the front and rear corners of the car to indicate the intended direction of turn to other drivers.
- Wiper Blade: Rubber blades on arms that sweep across the windshield to remove rain, snow, and debris for clear visibility.
- Radiator: A cooling system component located behind the grille, responsible for dissipating heat from the engine coolant to prevent overheating.
- Radiator Supports: Structural elements that hold and secure the radiator in place within the engine bay.
- Cowl Panel: The area at the base of the windshield, often housing the wipers and air intakes for the cabin ventilation system.
- Quarter Panel: The body panel located between the rear door and the trunk, extending around the wheel well. It’s a significant structural part of the car’s side.
- Fender (Wing or Mudguard): Body panels that frame the wheel arches. They prevent road debris from being thrown up by the tires and protect the car body.
- Fender Liners (Wheel Well Liners): Plastic or composite inserts within the fenders that provide additional protection to the car body from water, salt, and debris kicked up by the tires.
- Roof: The top panel of the car, providing protection from weather and contributing to the car’s structural integrity.
- Sunroof: An optional movable panel in the roof that can be opened to allow light and fresh air into the vehicle cabin.
- Mirrors (Side Mirrors and Rearview Mirror): Reflective surfaces that allow the driver to see areas beside and behind the vehicle, essential for safe driving.
- Doors: Hinged panels that provide access to the vehicle’s interior. Cars can have two or four doors depending on the design.
- Door Handle: Mechanisms used to open and close the car doors, available in various designs from traditional handles to modern electronic or flush designs.
- Window Glass: Transparent panels in the doors and around the car that allow visibility and protect occupants from the elements.
- Quarter Window: Smaller windows located behind the rear doors or in the C-pillar area, often in sedan or station wagon designs, enhancing visibility and light in the rear cabin.
- Trunk or Decklid (Boot): The hinged cover at the rear of the car that provides access to the cargo storage area.
- Mud Flaps (Splash Guards): Panels located behind the wheels, especially rear wheels, to minimize the spray of mud, water, and road debris onto other vehicles and the car itself.
- Wheels: Circular components that allow the car to move by rolling along the road surface, typically made of metal alloys and fitted with tires.
- Hubcap (Wheel Cap): Decorative covers for the center of the wheel, often used to protect wheel bearings from dirt and moisture and to enhance the appearance.
- Dashboard (Instrument Panel): The control panel inside the car, located in front of the driver, containing instruments displaying speed, fuel level, and other critical vehicle information.
- Number Plate (License Plate): A metal or plastic plate attached to the front and rear of the vehicle displaying the vehicle’s registration number for legal identification.
- Taillights: Lights at the rear of the vehicle, including brake lights, turn signals, and rear position lights, ensuring visibility and communication with other drivers, particularly in low light conditions.
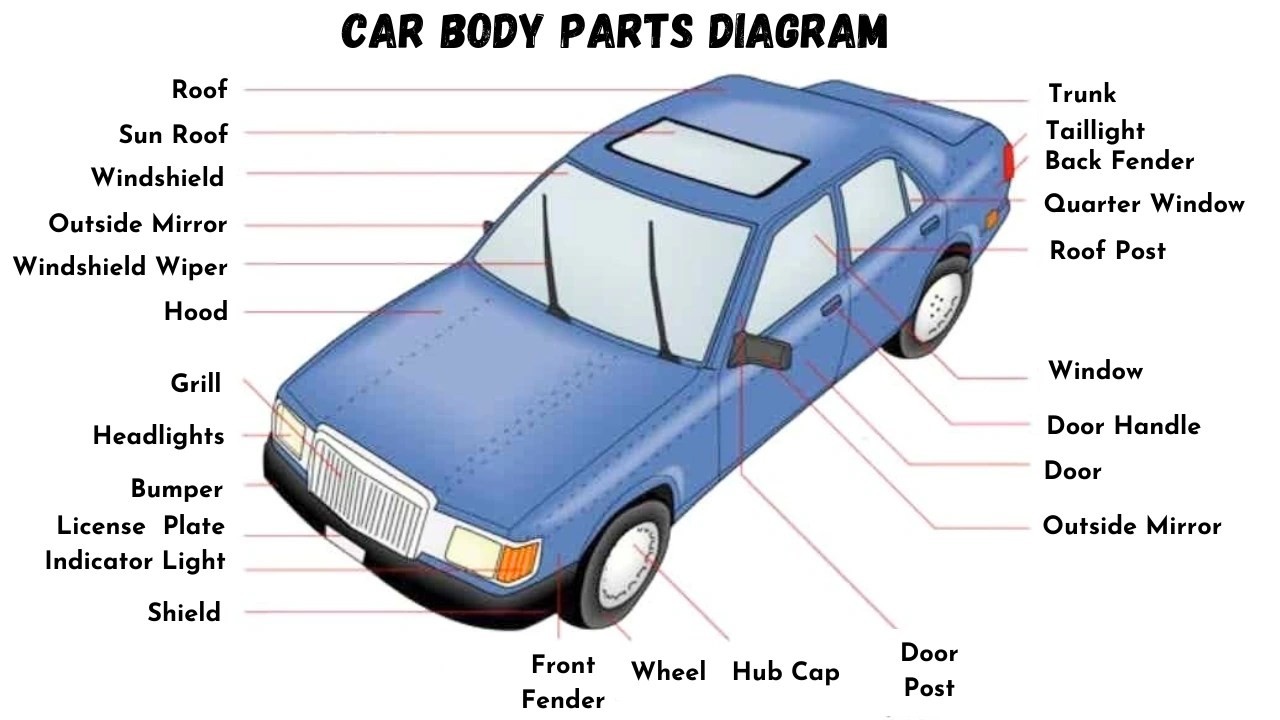 Car Body Parts Diagram
Car Body Parts Diagram
Alt Text: Diagram illustrating car all body parts name, clearly labeling exterior components such as hood, bumper, headlight, fender, door, roof, wheel, and trunk.
Detailed Insights into Car Body Components
Let’s delve deeper into some of the key car body parts and understand their functions and materials in more detail.
#1. Body Shell: The Foundation of Your Car
The body shell is essentially the skeleton of your car. It’s the main structural component upon which the engine, chassis, and all other parts are mounted. Think of it as the underlying framework that defines the car’s shape and ensures occupant safety. Modern body shells are designed with crumple zones to absorb impact in a collision, protecting the passengers inside.
#2. Hood/Bonnet: Protecting the Engine Bay
The hood, or bonnet in British English, is more than just a cover. It shields the engine and its vital components from the elements—rain, snow, and debris. It’s typically made of steel or aluminum for strength and lightness. The design of the hood can also impact aerodynamics and engine cooling, sometimes incorporating scoops or vents for performance enhancement.
#3. Front Bumper: First Line of Defense
The front bumper is designed to be the first point of contact in a minor collision. It’s engineered to absorb impact and minimize damage to the more expensive and critical parts of the car, such as the headlights, grille, and engine components. Bumpers are usually made of plastic, often reinforced with steel or energy-absorbing foam underneath for better protection.
#4. Rear Bumper: Protecting the Rear
Mirroring the function of the front bumper, the rear bumper protects the vehicle’s rear end. It often houses taillights and sometimes parking sensors. Rear bumpers safeguard the trunk, exhaust system, and rear body panels from damage during low-speed impacts.
#5. Bonnet Grill: Cooling and Style
The grille is more than just a design element; it’s crucial for engine cooling. By allowing air to flow into the engine bay, it helps regulate the engine temperature. Grilles are designed to be vehicle-specific and often contribute significantly to a car’s brand identity and aesthetic appeal. Materials can range from plastic to chrome and even carbon fiber for high-performance vehicles.
#6. Bullbars or Crash Guards: Enhanced Protection
Bull bars and crash guards are robust additions, typically made of metal, that offer extra protection to the front and sometimes rear of the vehicle. Originally designed for off-road vehicles to protect against animal collisions, they are also used in urban settings for added protection in minor impacts. However, their use can be controversial due to pedestrian safety concerns.
#7. Headlight: Illuminating the Path
Headlights are critical safety components, illuminating the road ahead during nighttime or low-visibility conditions. Modern headlights come in various technologies, including halogen, LED, and laser, each offering different levels of brightness, efficiency, and lifespan. Their design is also heavily integrated into the car’s overall styling.
#8. Fog Lamp: Enhancing Visibility in Poor Weather
Fog lamps are designed to cut through fog, mist, and heavy rain more effectively than headlights. Positioned lower to the ground, they illuminate the road surface beneath the fog layer, improving visibility and safety in adverse weather conditions.
#9. Signal Lights: Communicating Intentions
Signal lights, or indicator lights, are essential for communicating your driving intentions to other road users. They are positioned at the front and rear corners of the vehicle and blink to indicate turns or lane changes. Emergency lights, using all indicators simultaneously, enhance vehicle visibility in emergencies.
#10. Roof and Pillars: Structural Integrity and Protection
The roof provides essential protection from the elements and contributes significantly to the car’s structural rigidity, especially in rollover situations. Pillars are the vertical supports that hold up the roof. They are designated alphabetically from front to rear (A-pillar, B-pillar, C-pillar, and sometimes D-pillar), and they play a crucial role in crash safety and structural integrity.
#11. Doors and Windows: Access and Protection
Doors provide access to the vehicle’s cabin and are designed to protect occupants during side impacts. They incorporate features like door locks, power windows, and side impact beams for safety. Windows provide visibility and can be opened for ventilation (except for the windshield, which is fixed for structural reasons).
#12. Rear Panels: Housing Rear Components
Rear panels encompass the area at the back of the car, including taillights, the trunk lid, and the rear bumper. They are designed to integrate these components seamlessly and often house structural elements and safety features.
#13. Front Panels: Integrating Front Components
Front panels are the forward-facing body parts that integrate the headlights, grille, bumper, and fenders. Their design and construction are vital for aerodynamics, aesthetics, and pedestrian safety.
#14. Steering Wheel and Car Wheels: Control and Motion
While the steering wheel is an interior part, it’s directly related to the car’s body and exterior function. The steering system, including the steering wheel, column, and linkages, allows the driver to control the direction of the car’s wheels. Car wheels are the rotating components that enable movement, and their design and material impact handling, performance, and aesthetics.
#15. Front and Rear View Mirror and Windows: Visibility Aids
Mirrors and windows are crucial for driver visibility. Windshield wipers are an essential part of maintaining clear vision through the windshield in inclement weather. They consist of blades, arms, and a motor-driven system to sweep away water and debris.
#16. Fenders: Protecting from Road Debris
Fenders, also known as wings or mudguards, are designed to prevent road debris, water, and mud from being thrown up by the tires. They protect the car body from damage and keep the car and surrounding environment cleaner.
#17. Quarter Panels: Side Structural Elements
Quarter panels are significant side body panels that extend from the rear doors to the trunk. They are often integral to the car’s structural integrity and styling, wrapping around the rear wheel wells.
#18. Sunroof: Adding Light and Air
Sunroofs offer an opening in the car roof to let in natural light and fresh air. They can be manually operated or motorized and are available in various sizes and designs, enhancing the in-cabin experience.
#19. Wheels: Rolling Motion
Wheels are fundamental to a car’s mobility. They consist of a rim, which holds the tire, and a wheel disc or spokes, which connect the rim to the hub. Wheel design and materials are critical for performance, handling, and aesthetics.
#20. Windshield Washer Motor: Ensuring Clear Vision
The windshield washer motor pumps washer fluid onto the windshield to help the wipers clean away dirt and grime. It’s a small but vital component for maintaining clear visibility, especially in dirty or dusty conditions.
#21. Wiper: Clearing the Windshield
Wipers are the mechanical arms with rubber blades that sweep across the windshield. They are a crucial safety feature, ensuring the driver has a clear view of the road ahead in rain, snow, or when the windshield is dirty.
FAQs About Car Body Parts Names
What are common terms for car body parts?
Common body part names include hood (bonnet), bumper, fender (wing), door, roof, trunk (boot), wheels, and lights. These are fundamental components that make up the car’s exterior.
What are the panels on a car called?
The main panels are the hood, roof, doors, fenders, quarter panels, and trunk lid. These panels form the outer skin of the car and define its shape and style.
What is the most important part of a car’s body?
The body shell is arguably the most critical body part as it provides the structural foundation and safety cage for the vehicle and its occupants.
How can I find the right name for a car part?
Using online parts catalogs, consulting your car’s owner’s manual, or visiting a reputable auto parts store or dealership are effective ways to identify car parts names accurately. Providing your Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) can also help ensure you get the correct part name and description.
What is the front body of a car called in different regions?
In American English, the front body part covering the engine is called the “hood,” while in British English, it’s referred to as the “bonnet.”
Understanding “car all body parts name” is more than just automotive jargon; it’s practical knowledge that empowers you as a car owner or enthusiast. By familiarizing yourself with these terms, you can better understand your vehicle, communicate with professionals, and appreciate the intricate engineering that makes modern cars possible.